Filmmaker Brian Flemming documents his journey exploring Christianity by questioning the existence of Jesus, examining evidence that supports the Myth of a Christ against the existence of a historical Jesus, as well as examining other aspects of the religion such as the questions of ethics of indoctrinating children in schools at a young age with the fear of god and other principles of faith instilled in them institutionally.
Google or Wikipedia? Those of us who search online are getting referred more and more to Wikipedia. For the past two years, this free online “encyclopaedia of the people” has been topping the lists of the world’s most popular websites. But do we really know what we’re using? The Truth According To Wikipedia plunges into the story behind Wikipedia and explores the powerful world of ‘Web 2.0’ -- Is it a revolution, or pure hype?
Loose Change is a series of films that present evidence that the September 11, 2001 attacks were planned and conducted by elements of the United States government. The series also examines anomalies in the historical record of the attacks while drawing comparisons from some of the many mysterious and renowned events that have reshaped world history, such as the Reichstag Fire in 1933 that catapulted Hitler to dictatorship and the Gulf of Tonkin Incident in 1964 that led to the Vietnam War.
Jesus Camp follows several young children as they prepare to attend an event called 'Kids on Fire,' a Christian summer camp run by Becky Fischer. Through interviews with Fisher, the children, and others, Jesus Camp illustrates the unswerving belief of the faithful—a housewife and home-schooling mother tells her son that creationism has all the answers; footage from inside the camp shows young children weeping and wailing as they promise to stop their sinning; child after child is driven to tears. These scenes are contrasted with clips from another Christian radio host who is appalled by such happenings. Are these children being brainwashed?
9/11 Mysteries presents and analyses over 90 minutes of demolition evidence, laced with witness testimonials from key figures in the events of September 11th such as William Rodriguez -- a janitor from the North Tower of the World Trade Centre who was inside during the attacks. Moving from the myth through to analysis and into a discussion of the players, careful deconstruction of the official story is set alongside clear physics. How do you turn a 110-story building to dust in under ten seconds?
Supported by a mix of archival footage, NASA shots of burning oil fields and historical film excerpts, Crude Awakening examines peak oil. From Houston to Caracas, the Lake of Maracaibo, the Orinoco delta, Central Asia's secretive republic of Azerbaijan with its ancient capital Baku and the Caspian Sea, to London and Zürich. The film questions the future of oil with leading authorities such as oil investment banker Matthew Simmons, former OPEC chairman Fadhil Chalabhi, Caltec's head of physics, Professor David Goodstein, Stanford University political scientist, Terry Lynn Karl and peak oil expert, Matthew Savinar...
Crude Impact examines the interconnections of human economic activity, the use of fossil fuels and the effects that these have on the environment, the climate and humanity. What is peak oil? And what does this mean of the issue of global warming? The film also investigates the questionable practices of oil companies, to which there are plenty of examples...
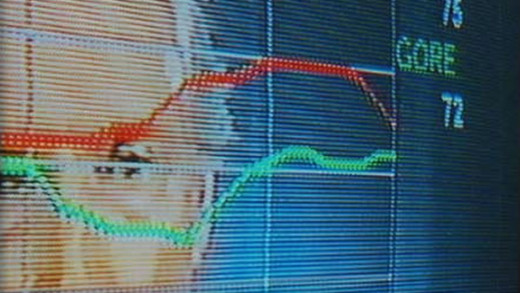
Why have a real election when you can just buy the result? In Bush Family Fortunes, Greg Palast examines various aspects of the Presidency of George W. Bush, including the very controversial 2000 US Presidential 'election' and of course, the invasion of Iraq. What are the Bush family connections?
The American Blackout chronicles the 2002 defeat, and 2004 re-election, of Congresswoman Cynthia McKinney to the U.S. House of Representatives, focussing on issues surrounding voter disenfranchisement and the use of electronic voting machines in both the 2000 and 2004 presidential elections...
The Yes Men are a culture-jamming activist-duo from the United States that are known for their impersonations of entities that they dislike as a form of protest. Using spoofed personas, they spread awareness of problematic social issues through the mainstream media. The two have also created and maintained fake websites, which have even led to numerous interviews, conferences, and TV invitations for their spoofed personas to espouse the truth about just how corporations and governmental organisations often act in dehumanising ways toward the unwitting public. In this film, we see how the two Yes Men take on the World Trade Organisation and confront the brutal realities of globalisation using satire and tactical media to get their message across, culture-jamming the corporate interest.
Using camera footage recorded by protesters at the scene of the World Trade Organisation riots in the United States during November 1999, Breaking The Spell documents the events of the time from the perspective of the activists, following the massive 'controversial' street protests and ensuing confrontations with police. Rather than attempting to cover every situation at the WTO, Breaking the Spell covers a few scenes in depth, filmed in the thick of the action, including footage that aired nationally on 60 Minutes...
Each year, legions of ad people, copywriters, market researchers, pollsters, consultants, and even linguists spend billions of dollars and millions of hours trying to determine how to persuade consumers what to buy, whom to trust, and what to think. Increasingly, these techniques are migrating to the high-stakes arena of politics, shaping policy and influencing how Americans choose their leaders. In The Persuaders, renowned media scholar Douglas Rushkoff explores how the cultures of marketing and advertising have come to influence not only what we buy, but also how we view ourselves and the world around us. The Persuaders draws on a range of experts and observers of the advertising and marketing world, to examine how, in the words of one on-camera commentator, “the principal of democracy yields to the practice of demography,” as highly customised messages are targeted to individuals using technology and fine-tuned social engineering techniques.
They spend their days sifting through reams of market research data. They conduct endless surveys and focus groups. They comb the streets, the schools and the malls, hot on the trail of the "next big thing" that will snare the attention of their prey -- a market segment worth an estimated $150 billion a year. They are the merchants of cool: creators and sellers of 'popular culture' who have made teenagers the hottest consumer demographic...
Imagine a home that heats itself, that provides its own water, electricity and spaces to grow food. One that needs no expensive technology, that recycles its own waste and that can be built anywhere, by anyone, out of garbage. Literally. Thirty years ago, architect Michael Reynolds imagined such a home and then set out to build. Today, there are strong communities of people living in these homes throughout the world, but all doesn't come without the constant resistance and hindrance from government and big business which are rightly threatened...
No Logo
In the age of the brand, logos are everywhere. But why do some of the world's best-known brands find themselves at the end of spray paint cans and the targets of anti-corporate campaigns? No Logo, based on the best-selling book by Canadian journalist and activist Naomi Klein, reveals the reasons behind the backlash against the increasing economic and cultural reach of multinational companies. Analysing how brands like Nike, The Gap, and Tommy Hilfiger became revered symbols worldwide, Klein argues that globalisation is a process whereby corporations discovered that profits lay not in making products (outsourced to low-wage workers in developing countries), but in creating branded identities people adopt in their lifestyles. Using hundreds of media examples, No Logo shows how the commercial takeover of public space, the restriction of 'choice', and replacement of real jobs with temporary work -- the dynamics of corporate globalisation -- impact everyone, everywhere...
Paraguay's Painful GMO Harvest reports on a nationwide peasant uprising against farmers of genetically-modified soya who are seen as colonists partly responsible for the almost total deforestation of the eastern provinces...
Neuroscientist Professor Susan Greenfield says today's developing brain is being worryingly reshaped by excessive visual stimulation -- the effect of a culture driven by screens. Biotechnology, nanotechnology, even the internet are all impacting on our brains and could be heralding future generations with different abilities, agendas and even ways of thinking. Her prediction is that we might be standing on the brink of a cataclysmic mind-makeover never before seen...
Advances in technology, global demand and the very essence of the commercial fishing industry itself means that whole species of wild fish are under threat. The species of fish that we eat today are predicted to be in a state of collapse by 2050 -- some are already extinct. Overfishing, or even more simply, the commercial fishing industry in general is to blame for this, along with celebrity chefs and 'exotic' restaurants; and mass consumer demand in today's world of globalisation. The End Of The Line documents the concerns and the processes behind commercial fishing and it's impact on the environment, the climate and the future existence of many species -- including our own...
Collapse
Collapse is a documentary film exploring the theories, writings and life story of controversial author Michael Ruppert, a former Los Angeles police officer turned investigative reporter who has authored books on the events of the September 11 attacks, documented widespread drug trafficking and other secret operations by the CIA, and written on the issue of peak oil and other energy issues. Using archival footage interspersed as illustration, Collapse explores Ruppert's conclusions that unsustainable energy and financial policies have led to an ongoing collapse of modern industrial civilisation...
Fool Me Twice
Fool Me Twice documents the Australian government's lies about the East Timor massacres, the cover-up of the Bali bombings (including the 1993 World Trade Centre attack) and subsequent anti-terror legislation forced through parliament by the Howard government. Laws that are still in effect today...
Uncounted documents how the election fraud that altered the outcome of the 2004 election led to even greater fraud in 2006 and now looms as an unbridled threat to the outcome of the 2008 and future elections. The film shows how easy it is to change election outcomes and undermine election integrity across the United States using electronic voting machines and even other simple methods of manipulation...
In the wake of the attacks of September 11th 2001, the United States opened a prison camp in Guantánamo Bay, Cuba. The hundreds of prisoners detained there are not afforded prisoners of war status according to the Geneva Convention, they are labelled "unlawful combatants" and are held indefinitely and tortured with no right to a lawyer or a trial. Gitmo -- The New Rules Of War cuts through the official political rhetoric surrounding Guantánamo to expose what really goes on at the United States central gulag in the 'war on terror'.
Filmed in Thailand and the Philippines in July 2007, Squeezed tells the story of how free trade agreements and globalisation are changing the lives of millions of people living in the Asia-Pacific region with APEC. Featuring interviews with farmers, workers and slum-dwellers, the film travels across the landscapes of Asia, from the lush rice paddies of Thailand to squatter settlements perched on a rubbish dump in urban Manila. Documenting these contrasts and contradictions, Squeezed accounts the impact of globalisation...
Is genetic engineering really dangerous? The manufacturers claim that genetically modified food "produces higher yields, fights world hunger, and reduces the need for pesticides." But at what cost? Following the Trail questions whether any solid testing has been done to determine the safety and risks of genetically engineered foods and examines evidence to test the veracity of the claims made by genetic engineering corporations that the foods produce 'higher yields, fight world hunger' etc...
As the biotechnology industry spends more than $50 million a year to convince us that 'genetic technology' is our only hope for feeding the world and saving the environment, toxic agricultural chemicals continue to poison the air, food and water and put farm workers in serious danger. So what's the real problem? Using archive footage and interviews with farmers, scientists, government officials and activists, Fed Up With Genetic Engineering presents an overview of the current food production system, exploring the impacts of pesticides, the resistance of biotechnology companies to food labelling and the links between government officials and major biotechnology and chemical companies...
Robert Beckford visits Ghana to investigate the hidden costs of rice, chocolate and gold and why, 50 years after independence, a country so rich in 'natural resources' is one of the poorest in the world. He discovers child labourers farming cocoa instead of attending school and asks if the activities of multinationals, the World Bank and International Monetary Fund have actually made the country’s problems worse...
Good Copy Bad Copy is a documentary about the current state of copyright and culture in the context of Internet, peer-to-peer file sharing and other technological advances. Featuring interviews with many people with various perspectives on copyright, including copyright lawyers, producers and artists, Good Copy Bad Copy documents that "creativity itself is on the line" and that a balance needs to be struck, or that there is a conflict, between protecting the right of those who own intellectual property and the rights of future generations to create...
Could a media system, controlled by a few global corporations with the ability to overwhelm all competing voices, be able to turn lies into truth? This documentary examines the relationship between the media, corporations, and government. In a country where the top 1% control 90% of the wealth, the film argues that the media system is nothing but a subsidiary of the corporate world. Have we entered an Orwellian world of doublespeak where outright lies can pass for the truth?