Pornography is now more easily accessible than ever before--it's a click away on the internet. And many men are finding their everyday relationships in impacted because of their porn addiction. This documentary examines the problem and explores growing evidence that there is a chemical basis in the brain for the condition, related to dopamine, uncovering the human costs of porn addiction along the way. The film follows some real life examples of people battling their addiction, as well as reviewing some cases where addiction has unravelled with tragic results. But as with any addiction, the good news is that it can be turned around...
This culture runs on algorithms on a scale never before realised. Whether you get a job or a mortgage or insurance or healthcare, how you get from A to B, how huge fortunes are made or whom is driven into poverty, decisions on whom is sent to or released from prison, whom is voted for in manipulated elections--the reach of algorithms has captured so much of the major decisions of our lives, all in complete obscurity, inscrutable. So what are the implications of this? What sort of 'decisions' do machines make, to which we've come to regard as infallible and impartial, accurate and precise? Algorithms Rule Us All speaks to data scientists and programmers themselves to answer the question of what they think is unfolding with the so-called Big-Data society and how we're continuing to hand over our lives and societies to the whim of machines that are driven by rapacious profit-driven companies, for the goal of commodification of everything. What are the implications for human autonomy, society, democracy?
In a quarter of a century, the Amazon corporation has propelled Jeff Bezos from 'online bookseller' to technology behemoth. He is the richest man on the planet, and the company he founded is one of the most powerful in the world. This documentary investigates Amazon's rise to corporate rein, revealing the problematic inside-operations that have the public tethered to its services. Former high-level insiders describe Amazon's obsessive data-gathering operations, that enable the company to use what it knows about us to shape not only the future of retail, but the workplace and technology in synergy. On both sides of the world, politicians and regulators are tardily beginning to question Amazon's power. But can the public rein in this corporate empire and break its addiction before even more damage is done to the structure of society and the environment?
In recent years, nature conservation has become a booming business where huge sums of money change hands, and endangered species become exotic financial products. Banking Nature, delves into this hidden world of so-called environmental banking, where huge corporations such as Merrill Lynch and JP Morgan Chase buy up the land and habitat of endangered species, and then sell them in the form of shares. Companies that inevitably harm the environment are then obliged to buy credits to offset the damage that they have caused. In Uganda, we meet men who measure trees to determine how much carbon they store and then a banker from the German firm that sells the resulting carbon credits. In Brazil, the steel giant Vale destroys the rainforest, replaces it with a monocrop tree plantation, and reaps the benefits of environmental credits as if the rainforest was still standing. Banking Nature posits that we disallow the same corporate criminals responsible for the global financial crisis from turning what's left of the natural world into their final corrupt commodities market.
How do our families influence our relationship with our own bodies? How does popular culture's standards of beauty get inside our hearts and heads? In what ways can sport and the drive for fitness actually make us sick rather than healthy? In Beauty Mark, former champion triathlete Diane Israel examines this culture's unhealthy fixation on thinness, beauty, and physical perfection. She talks candidly about her own struggle with eating disorders and obsessive exercising, confronting her own past to come to terms with this culture's unhealthy fixation on self-destructive ideals of beauty and competitiveness.
Fuelled by popular personalities on Instagram, YouTube and Snapchat, cosmetic surgery is pushing further into the mainstream. Huge numbers of people, predominantly young women, are choosing to alter their appearance forever as though it's as simple as buying a new set of clothes. Social-media "influencers" get free procedures in exchange for promoting certain doctors or agencies or products to their audiences. Going on the numbers alone, audiences seem to respond to this blatantly cacophonous advertising, following their social media stars closely, and taking out huge personal loans to get surgery and "keep up with the Kardashians." Doctors offering the surgery are even becoming media stars themselves, and it's redefining the meaning of doctor/patient relations. Underpinning this entire industry, is a business model of targeting women who can barely afford procedures by selling the dream of a "new you." Social-media laps it up, and the cycle repeats. But as this investigation shows, when things go wrong, the physical and financial costs are devastating. Real doctors who are left to pick up the pieces, are warning that the booming industry is creating a dangerous legacy, and not just to the concept of beauty.
Burned: Are Trees the New Coal? investigates the latest method of providing so-called "green" electricity, as espoused by the renewable energy movement. It's called biomass, which is a euphemism for clear-cutting and burning forests. It is claimed that this is first a sustainable method of electricity creation, but secondly, and more slanderous, is claimed to be carbon-neutral and environmentally friendly. So how did this become the purported saviour for the power-generation industry, and by extension, the modern environmental movement? Burned provides a visceral account of these questions, while documenting the accelerating destruction of forests to fuel this destructive culture.
Mental illness and suicide have become the greatest threats to school-aged children. Many parents still view dangers to children and teens as primarily physical and external, but they're missing the real danger: young people spending more time online and less time engaging in real life, free play, and autonomy. While older generations might have learned the value of being outside, household chores, and in-person playtime with friends, the youth of today have fallen prey to smartphones and video games. Childhood 2.0 is an exploration of this dramatic technological and cultural shift, where children and parents face the rise of social networks, mobile devices, and the screen culture, along with addiction, withdrawal, anxiety, depression, online abuse, bullying, the pervasiveness of pornography, sexting, the rise of online pedophilia and sexual predators, the loss of playtime, imagination and autonomy, and the rapid growth of suicide among children and teens. In addition to mental health professionals, the filmmakers speak with a series of concerned parents who have witnessed a profound transformation in their children, especially when placed in contrast to their own beginnings. Then there are the children themselves who speak to the overpowering allure of their devices, the pressures these devices place on them in their daily lives, and the challenge they face when they try to turn away from the screen.
Facebook is an enormously powerful corporation, harnessing both the self-disclosed and gleaned personal data of over 2 billion people. Its user-base is larger than the population of any country. The company is all pervasive online, tracking and profiling users and non-users alike. Cracking the Code looks at the insides of this giant machine and how Facebook turns your thoughts and behaviours into profits--whether you like it or not. And it's not just a one-way transaction either. Cracking the Code also explains how Facebook uses vast troves of web data to manipulate the way you think and feel, as well as act--all in the sole interests of Facebook, masquerading as "community." What are the social implications of this--when one company basically controls the insights and experiences of the entire online world, with extremely personalised and targeted social and behavioural engineering on a scale never before seen?
Facing Beauty
Facing Beauty examines the explosive growth of the plastic surgery industry, by looking through China's beauty obsession and the social media influencers that are driving its mindset. A mobile app has captured the population by promoting an "ideal ratio in human facial features," where users' faces are assessed and given a score. The app then draws up plans for surgeries to lower that score, referring users to endorsed clinics, driving both non-invasive and invasive surgeries and procedures. Now, demand for those procedures is so widespread among the country's youth population, it's estimated the industry will be worth US$200 billion by 2030. This growth in the industry has led to an expansion of 'beauty' institutions that employ staff without adequate medical qualifications or protections, and even though some procedures have been banned and the negative health impacts shown, demand continues to increase at fever pitch.
Over the past three decades, obesity rates in the United States have more than doubled for children and tripled for adolescents, and a startling 70% of adults are now obese or overweight. The result has been a widening epidemic of obesity-related health problems. But while discussions about this crisis tend to focus solely on the need for individual responsibility and more exercise, Feeding Frenzy turns its focus squarely on the responsibility of the processed food industry and the outmoded government policies it benefits from. It lays bare how government subsidies designed to feed the hungry during the Great Depression have enabled the food industry to flood the market with a rising tide of cheap, addictive, high calorie food products, and offers an engrossing look at the tactics of the multi billion-dollar advertising industry that makes sure that everyone keeps consuming.
Generation Wealth is a visual history of the materialistic, image, and celebrity-obsessed culture, explored through the work of photographer and filmmaker Lauren Greenfield. Part historical essay, part autobiographical, Greenfield puts the pieces of her life's work together to reveal the pathologies that have created the richest and most unequal society the world has ever seen. Spanning consumerism, beauty, gender, body commodification, aging, and sex, Generation Wealth unpacks the global boom-bust economy, the corrupt American Dream and the human costs of capitalism, narcissism and greed.
In the race towards modernity, amongst the buzz and jitter of technological innovation and the rapid growth of cities, silence is now quickly passing into legend. Beginning with an ode to John Cage's seminal silent composition 4' 33", the sights and sounds of this film delicately interweave with silence to create a contemplative experience that works its way through frantic minds and into the quiet spaces of hearts. As much a work of devotion as it is documentary, In Pursuit of Silence is a meditative exploration of our relationship with silence, sound, and the impact of noise on our lives.
How has a culture of readily-accessible and ubiquitous pornography that is largely free-to-view on laptops, mobile phones, and televisions, shaped young peoples' nascent ideas and expectations of love, sex and relationships? This short follows a group of teenagers who, with unflinching honesty and realism, reflect on the influence of porn on their lives. Has it changed their sexual tastes and behaviours? What are the differences between boys and girls in their approach to porn? What is the effect of the porn industry's move into ever more hardcore scenes? With exclusive behind the scenes access to the stars and directors at the centre of the international porn industry in LA and Budapest, Love and Sex in an Age of Pornography provides intimate insights into all sides of the porn industry--from the gritty details of porn's production, to its effects on curious youngsters.
Love Child
In 2010, the death of a three-month-old baby in South Korea named Sarang (translated as Love) became an international news story—the parents had neglected her to play an online fantasy game. She died primarily of malnutrition. But instead of merely condemning the parents, Love Child takes a different approach by looking at some issues that led to the parents addiction and how their child became oblivious to them. The film then expands to view the way South Korea's standing as a world leader in Internet technologies has adversely affected its society, speaking also globally, where the virtual world now trumps the real world for many millions of people, with extreme consequences.
The combination of detailed descriptions by abused women and great dramatisations helps both male and female viewers to understand the realities of spousal abuse, what motivates this kind of activity, and reveals the myths that surround it. Low self-esteem, rather than straight anger, is the central causal issue and the ability to quit habitual spousal abuse is as problematic as recovery from any other addiction.
Over 18
Over 18: The Question is Not Enough is a broad examination of modern pornography. For just a generation ago, porn was on the fringe in glossy magazines. Today, porn is mainstream and even celebrated. But as softcore imagery migrated into popular culture through advertising and became normalised, today's mainstream porn is hardcore and explicit in order to distinguish itself. Now too, with the pervasiveness of the Internet, graphic video is also increasingly exposed to young people. Over 18 tells the story of Joseph, a 13-year-old boy who is recovering from a porn addiction that he fell into when he was just 9 years old--a case that is not unexceptional. By exploring what today's mainstream porn is and how it captures people through candid interviews with porn producers and ex-porn stars themselves, Over 18 also provides research from academics, and life experience from recovering addicts, to take aim at the content of modern pornography and its existence as an industry.
Through powerful insider information, Pack of Lies reveals the deception of the tobacco industry's claims that they do not seek to addict children to nicotine. The film provides important analytical background. Jean Kilbourne is a nationally recognized researcher and lecturer on media, advertising, and health issues. Rick Pollay teaches advertising and marketing management at the University of British Columbia, and has been an expert witness in trials involving the tobacco industry. They team up to provide important insights on the power of advertising dollars to counter the influence of scientific research, to affect news coverage, and to put private profit ahead of public health.
One generation from now, most people in the United States will have spent more time in the virtual world than in the natural world. New media technologies have changed lives in countless ways. Streams of information now appears in a click. Overseas friends are contactable in an instant. Engulfing video games and streams of endless entertainment to stimulate the senses, dazzle the mind and pander to the acculturated desire to be in control. Even grandma loves Wii. But what are people missing when they're behind screens? How is it already impacting our children, our society, and the planet? At a time when people are at screens more than they are outside, Play Again explores the challenge in dealing with the addiction and returning to the real world...
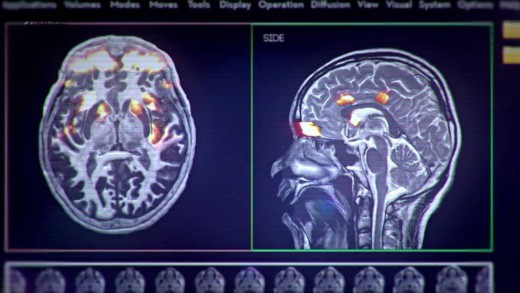
Martin Daubney walks away from his position as editor of a renowned porn magazine after becoming a father. With his son, now four years old amongst the confusion by contradictory headlines, and driven by the knowledge that his boy will soon reach the age at which most children first see porn--10 years old--Daubney wants to find some answers. How does pornography effect kids? Where is the evidence? Porn on The Brain takes us through the journey, and Daubney discovers that porn has changed from what he remembers as a teenager--today's porn is extreme, it's free, it's pervasive and only one click away, and Daubney is shocked by the content. Porn on The Brain reviews internationally-renowned neuroscientists, leading therapists and educators who are all concerned about the effects on vulnerable teenage brains today of free and easy access to hardcore pornography. The film includes the shocking results of a specially-commissioned survey of teen porn habits, conducted for the documentary by the University of East London; and collaborates with the University of Cambridge to conduct the first study of its kind, scanning the brains of men who feel they are addicted to porn. When will we acknowledge that there is a problem?
Pornland
Pornography has moved from the outskirts of society into the very mainstream of this culture in over less than a span of a generation. From MTV to Internet pornography everywhere, pop culture industries continue to bombard all of us with sexualised images of idealised women and men that jump off the screen and go straight into our lives, profoundly shaping our identity, the ideas and acceptability of body image, and our most intimate relationships. In this video essay, based on the book of the same name, leading scholar and activist Gail Dines argues that the dominant images and stories disseminated by the porn industry, produce and reproduce a system that perpetuates social inequality and encourages violence against women at its very core. In direct opposition to the claims that pornography has delivered a more liberated, equitable and edgy sexuality, Pornland reveals a mass-produced vision of sex that is profoundly sexist, destructive and pervasive in this culture—a world that severely limits and undermines our collective ability to live authentic, truly equal relationships, free of systemic violence and degradation.
Public Figure
Public Figure is a measured exploration of this culture's obsession with social media, exemplified through the lives of several Instagram "influencers." The film invites the viewer to question how much of what we see online is real or delusion, while slowly, the "influencers" themselves reveal the extent to which they've completely commodified their lives into enterprises, as giant advertising engines, while also touching on the personal impacts of screen culture addiction. These commentaries are contrasted by views from clinical psychologists and counsellors, whom also question the long term effects of social media culture. While some figures use their commodified lives to inspire, promote a cause, or market their business, all in all, each and every "influencer" is wittingly or unwittingly part of a multi-billion dollar advertising engine that spends more money on marketing than education in the United States. Instagram advertisers will spend $2.38 billion on "influencers" in 2019. Public Figure asks us to reflect on our personal social media use, while questioning how society perceives reality.
The average child in the United States spends 40+ hours per week consuming media—the equivalent of a full-time job. This means that by the time children born today turn 30, they will have spent an entire decade of their lives in front of a screen. Remote Control examines the implications of this unprecedented level of exposure by showing the media habits of two families and supplementing their personal insights with interviews from media experts and educators. Revealed is the centrality of media in our lives and far-reaching effects that we are only beginning to understand, as well as ways we might begin to help our children live a life instead of watching one.
Physician and mother of two Dr. Delaney Ruston became interested in how much screen time is too much when her preteen started begging for a smartphone. Ruston saw other parents equally confused on how to balance technology with a young developing mind, so she decided to delve into the science behind screen time to understand how it affects young people's minds and development. Through personal stories and input from leading researchers, the result is Screenagers, a film that sheds light on the impact screen time is having on kids; exploring how learning, playing, and socialising online effects teens' developing attention span, fragile self-esteem, and moral instincts. Screenagers examines the real risks of failing in school, social isolation, and digital addiction. It also explores solutions to handle screen time and provides parents with tools to help young people develop self-control and find balance in their digital lives, rather than rapid-fire thumbs and a six-second attention span.
There are billions of people increasingly glued to 'smartphones' and consumed by the seemingly endless spectacle of 'social media.' But why? Reporter Hilary Andersson seeks to answer this question by tracking down insiders who reveal how social-media companies have deliberately developed habit-forming technology to get people addicted. Former Facebook manager, Sandy Parakilas, tells us the "goal is to addict you and then sell your time." Likewise, Leah Pearlman, the co-creator of the renowned 'Like' button, warns of the dangers of social-media addiction. Through these voices, and many others, Andersson shows how behavioural science is profoundly used by tech companies to keep people endlessly checking their phones, to the end of huge profits.
We live in a world of screens. The average adult spends the majority of their waking hours in front of some sort of screen or device. We're enthralled, we're addicted to these machines. How did we get here? Who benefits? What are the cumulative impacts on people, society and the environment? What may come next if this culture is left unchecked, to its end trajectory, and is that what we want? Stare Into The Lights My Pretties investigates these questions with an urge to return to the real physical world, to form a critical view of technological escalation driven rapacious and pervasive corporate interest. Covering themes of addiction, privacy, surveillance, information manipulation, behaviour modification and social control, the film lays the foundations as to why we may feel like we're sleeprunning into some dystopian nightmare with the machines at the helm. Because we are, if we don't seriously avert our eyes to stop this culture from destroying what is left of the real world.
Sugar Coated investigates a once secret public relations campaign, dating back to the 1970s, where the sugar industry deflected threats to its multi-billion dollar empire from scientific research emerging implicating processed sugar with adverse health effects. In order to continue sweetening the world's food supply, thus securing continued profits, the sugar industry turned to the very same deceptions and tactics lifted from the tobacco industry. Using big sugar's own internal documents on this strategy, Sugar Coated reveals the well-oiled tricks of the trade to confuse the public about what is really driving the global pandemic of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Will we be fooled again?
When modern antidepressants like Prozac were launched in the late 1980s, they were quickly heralded as wonder drugs for treating anxiety and depression with few side effects. While many say they have benefited from taking the drugs, there is an increasing body of evidence that reveal physical and mental side effects of the drugs that are wide-ranging and are often downplayed. From headaches and brain fog, to loss of sexual function and suicidal thoughts. The Antidepressant Story speaks to patients grappling with side effects such as these and asks if this multi-billion dollar pharmaceutical industry is really helping.