With the recent global financial crisis, governments across the world promised decisive action -- the biggest financial stimulus packages in history, along with gargantuan bail-outs of corporations and floods of money into private banks and investment firms. But what crazed logic is this: propping up bad debt with…more bad debt? Overdose reviews the happenings of the bail-outs over these years, showing how dangerous the situation continues as a burst bubble is re-inflated globally. What happens next?
The Spider's Web: Britain's Second Empire shows how Britain transformed from a colonial power into a global financial power. At the demise of empire, the City of London's financial interests created a web of offshore secrecy jurisdictions that captured wealth from across the globe and hid it behind obscure financial structures, and webs of offshore islands. Today, up to half of global offshore wealth may be hidden in British offshore jurisdictions, and these are now the largest players in the world of international finance. Based in part on the book Treasure Islands by expert Nicholas Shaxson, and through contributions from former-insiders, academics, and campaigners for justice, The Spider's Web reveals how, in the world of international finance, corruption and secrecy have prevailed over regulation and transparency, and how the United Kingdom is a pioneer of the modern corrupt global economy.
Dirty Money
In the late 1990s, the Reserve Bank of Australia thought it was on a winner. The bank had developed the technology to create polymer bank notes that it claimed rivalled paper money. So the Reserve Bank decided to set up a subsidiary company called Securency to sell the technology to the world. It had just one problem though—getting legitimate access to other central bank officials to pitch the idea. So instead, Securency decided to employ a shadow network of local "fixer agents" to make "connections" with relevant officials, lavishing them with prostitutes, cash, and bribing them into deals. Dirty Money is the story of this institutional corruption at the highest level of finance in Australia.
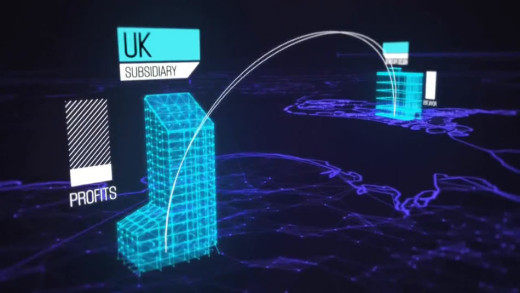
The Tax Free Tour travels the globe to expose the workings of offshore tax havens and the elite banking systems of the world's billionaires which operate in extreme secrecy. Using examples from multi-national corporations such as Apple Computer and Starbucks, the film traces sizeable capital streams that travel the world literally in milliseconds--all to avoid local laws and paying tax. Such routes go by resounding names like 'Cayman Special', 'Double Irish', and 'Dutch Sandwich'. The Tax Free Tour is a sobering look at how the world's rich live in an entirely different world than the rest of us...