The War at Home: The Untold History of Class War in the United States is a series that traverses the history of the labour movement and state repression in the United States. The series looks at history through the lens of the working class, from the Haymarket massacre in Chicago in 1886 to the Jim Crow spread in Louisiana, to the Triangle Shirtwaist tragedy of 1911, to the violent strikes and police raids of the Great Depression, and beyond. The series makes the connection between the purging of radicals from unions and the decline of union power in the 1920s, towards the 1960s and beyond.
Behind the Screens explores how Hollywood movies have largely become vehicles for the ulterior motives of advertising and marketing by the studios and media owners, rather than genuine storytelling or simple entertainment in their own right. By showing examples from popular movies such as Wayne's World, Forrest Gump, The Lion King, Summer of Sam, and Toy Story, this documentary demonstrates how this trend toward hypercommercialism—through product placement, tie-ins, merchandising and cross-promotions—comes to define the modern movie. What are the problems with this, as well as the cultural and social impacts? Combined with analysis from film scholars, critics, political economists, and an Oscar-nominated screenwriter, Behind the Screens presents accessible arguments to these questions.
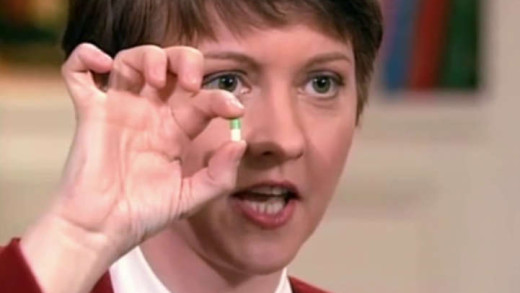
When modern antidepressants like Prozac were launched in the late 1980s, they were quickly heralded as wonder drugs for treating anxiety and depression with few side effects. While many say they have benefited from taking the drugs, there is an increasing body of evidence that reveal physical and mental side effects of the drugs that are wide-ranging and are often downplayed. From headaches and brain fog, to loss of sexual function and suicidal thoughts. The Antidepressant Story speaks to patients grappling with side effects such as these and asks if this multi-billion dollar pharmaceutical industry is really helping.
To many in both business and government, the triumph of the self is the ultimate expression of democracy, where power is truly moved into the hands of the people. Certainly the people may feel they are in charge, but are they really? The Century of the Self tells the untold and controversial story of the growth of the mass-consumer society. How is the all-consuming self created, by whom, and in whose interest?
The Truth About Killer Robots considers several cases where humans have been killed from interactions with automatic machines. From the Volkswagen factory in Germany, to workers in Chinese sweatshops assembling smartphones, to a bomb-carrying police droid in the United States, the film exposes this culture's fundamental fascination with machines, while illustrating the insatiable expansion of capitalism via automation and machine redundancy. Also explored are 'self-driving' cars; surveillance devices; humanless-stores, automated pizzas, robotic supermarkets and hotels; so-called 'sex' robots; and vast data gathering machines such as Facebook, which have subverted notions of real human interaction and intimacy. Told through the machine lens of engineers themselves, journalists and philosophers, the film attempts to go beyond the deaths of humans to reveal some of the ways that robots affect this culture in general. Not just by the displacement of labour, but fundamentally as humans of this culture adjust their lives to the rhythms of more and more machines, basic human faculties atrophy, and true connection to the real world and each other becomes more remote and strenuous, at precisely the same time where we need each other the most.
Up the Yangtze
Up the Yangtze focuses on the people affected by the building of the Three Gorges Dam across the Yangtze river in Hubei, China. Countless ancient villages and historic locales will be submerged, and 2 million people will lose their homes and livelihoods. The theme of the film is the rapacious transition towards consumer capitalism from a traditional farming and peasant-based society...
The Big Sellout reveals the reality of privatisation and globalisation by examining the corporate takeover of basic public services throughout the world, such as water supply, electricity, public transportation, and public health care. In South America, Asia, Africa, but also in Europe and the United States, filmmaker Florian Opitz talks to the architects of the new economic world order, as well as to ordinary people who have to deal with the real direct effects. The result is a tapestry of narratives the world over that show where the dogma of privatisation cames from, who profits from it, what societies lose, and why resistance is so important.
How to Let Go of the World and Love All the Things Climate Can't Change travels the globe, from New York City to the Marshall Islands and China, to meet with people who are committed to reversing the tide of global warming. The film examines the intricately woven forces that threaten the stability of the climate and the lives of the world's inhabitants.
For years, regulatory agencies and environmental groups have insisted that the increase in whale deaths off the East Coast of the United States has nothing to do with the rapidly-expanding wind industry's high-decibel pile driving, sonar mapping, and boat activities, to install wind-harvesting facilities for electricity generation. Thrown To The Wind travels to parts of the ocean where these activities are underway, to investigate these claims, showing that indeed these industrial activities are impacting critically endangered species in profound ways--which are being systematically ignored, while the climate and ecological crisis rages.
The Mayfair Set is a four part series that studies how capitalists overtly and surreptitiously came to prolifically shape governments during the 1980s, epitomised by the Thatcher government in Britain at the time. But the corporate influence of political power doesn't simply arrive, it rather culminates after decades of engineering rooted in the economic collapse from the aftermath of the Second World War. This series focuses on the unreported and almost unseen approach that capitalists have taken since the 1940s to gradually take control of the political systems of not only the United States and Britain, but elsewhere around the world—exemplified by the boom of globalisation.
If a crime is committed in order to prevent a greater crime, is it excusable? Is it, in fact, necessary? The Reluctant Radical follows Ken Ward as he confronts his fears and acts on these questions to stop climate change. After twenty years leading some of the most renowned mainstream environmental organisations, Ken witnesses first-hand how ineffective and unthreatening they are. As their efforts fail, and environmental collapse increases in scope and speed, Ken comes to see how direct action civil disobedience is the most effective political tool to deal with catastrophic circumstances. Ken breaks the law, to fulfil his obligation to future generations, to stop the oil economy. By following Ken for a year and a half through a series of direct actions, this film culminates with his participation in the coordinated action that shut down all the tar-sands oil pipelines in the United States on October 11, 2016. The film reveals the personal costs but also the true fulfilment that comes from following one's moral calling, even if that means breaking the law and its consequences. Ken has no regrets.
The Wall Street Code explores the once-secret lucrative world of prolific algorithmic trading by profiling an inside programmer who, in 2012, dared to stand up against Wall Street and its extreme culture of secrecy, to blow the whistle on insights into the way the modern global money market works. His name is Haim Bodek—aka 'The Algo Arms Dealer'—and having worked for Goldman Sachs, his revelations speak to the new kind of wealth made only possible by vast mathematical formulas, computer technologies and clever circumventions of laws and loophole exploits. Vast server farms and algorithms working beyond the timescale of human comprehension, have largely taken over human trading on the global financial markets for decades. What are the implications of that? The algorithms seem to have a life of their own. Snippets of code secretly lie waiting for the moment that your pension fund gets on the market; trades done in nanoseconds on tiny fluctuations in stock prices. And the only ones who understand this system are its architects—the algorithm developers. The Wall Street Code provides just a small insight into this new world of high-frequency trading, amongst other things...
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, is spouted as the ability of machines to "think" [sic] at a speed and depth far beyond the capacity of any human. Proponents of these digital technologies claim their systems are used in ways that are beneficial for society. But as we see, the current use of AI isn't necessarily aligned with the goals of building a better society. There still remain escalating concerns about labour, the future of work, privacy, the surveillance society, and social control--all valid criticisms that go back many decades--while the rivalry for technological supremacy between the United States and China mirrors the dynamics of the cold war. In the Age of AI is an investigation that touches on these areas, providing a platform to ask fundamental questions about unrestrained technological escalation.
Consumer capitalism dominates the economy, politics, and culture of our age, despite a growing trove of research showing that it is a failed system. In this illustrated presentation, media scholar Justin Lewis makes a compelling case that capitalism can no longer deliver on its myth of the dream and its promise to enhance the quality of life. He argues that changing direction will require changing our media system and our cultural environment, as capitalism has become economically and environmentally unsustainable. This presentation explores how the media and information industries make it difficult to envision other forms of life by limiting critical thinking and keeping us locked in a cycle of consumption, and shows us that change will only be possible if we take culture seriously and transform the very way we organise our media and communications systems.
Shifty
Shifty is a series of films that traverse the past 40 years in Britain, showing how the shift of political power to finance and hyper-individualism came together in powerful ways, to undermine one of the fundamental structures of mass democracy--the shared idea of what is real. As that fell apart, with it went the language and the ideas that people had turned to for the last 150 years to make sense of the world they lived in. As a result, life in Britain and the current and former colonies of its empire, has become strange--a hazy dream-like flux, where distrust in politicians keeps growing, and the political class seems to have lost control. Through archive footage, news reels, and on-screen-text in video essay format, Shifty documents the shapes of how this happened, using the vast ranges of footage to evoke what if felt like to live through an epic transformation during the 1980s.
By comparing the confluence of ideas about modifying behaviour using shock therapy and other forms of sensory deprivation (which culminated in the top-secret CIA project called MKULTRA during the 1950s) alongside the metaphor of similar shock treatment modifying national economics using the teachings of Milton Friedman and the Chicago School of economics, The Shock Doctrine presents the workings of global capitalism in this framework of how the United States, along with other western countries, has exploited natural and human-engineered disasters across the globe to push through reforms and set-up other mechanisms that suit those in power and 'shock' other countries into a certain wanted behaviour. Chronologically, some historical examples are the using of Pinochet's Chile, Argentina and its junta, Yeltsin's Russia, and the invasion of Iraq. A trumped-up villain always provides distraction or rationalisation for the intervention of the United States—for example, the threat of Marxism, the Falklands, nuclear weapons, or terrorists—and further, is used by those in power as more justification for the great shift of money and power from the many into the hands of the few(er).
Tracing the Internet's history as a publicly-funded government project in the 1960s, to its full-scale commercialisation today, Digital Disconnect shows how the Internet's so-called "democratising potential" has been radically compromised by the logic of capitalism, and the unaccountable power of a handful of telecom and tech monopolies. Based on the acclaimed book by media scholar Robert McChesney, the film examines the ongoing attack on the concept of net neutrality by telecom monopolies such as Comcast and Verizon, explores how internet giants like Facebook and Google have amassed huge profits by surreptitiously collecting our personal data and selling it to advertisers, and shows how these monopolies have routinely colluded with the national security state to advance covert mass surveillance programs. We also see how the rise of social media as a leading information source is working to isolate people into ideological information bubbles and elevate propaganda at the expense of real journalism. But while most debates about the Internet focus on issues like the personal impact of Internet-addiction or the rampant data-mining practices of companies like Facebook, Digital Disconnect digs deeper to show how capitalism itself turns the Internet against democracy. The result is an indispensable resource for helping viewers make sense of a technological revolution that has radically transformed virtually aspect of human communication.
Would any sane person think dumpster diving would have stopped Hitler, or that composting would have ended slavery or brought about the eight-hour workday; or that chopping wood and carrying water would have gotten people out of Tsarist prisons; or that dancing around a fire would have helped put in place the Voting Rights Act of 1957 or the Civil Rights Act of 1964? Then why now, with all the world at stake, do so many people retreat into these entirely personal "solutions"? Why are these "solutions" not sufficient? But most importantly, what can be done instead to actually stop the murder of the planet?
The Spider's Web: Britain's Second Empire shows how Britain transformed from a colonial power into a global financial power. At the demise of empire, the City of London's financial interests created a web of offshore secrecy jurisdictions that captured wealth from across the globe and hid it behind obscure financial structures, and webs of offshore islands. Today, up to half of global offshore wealth may be hidden in British offshore jurisdictions, and these are now the largest players in the world of international finance. Based in part on the book Treasure Islands by expert Nicholas Shaxson, and through contributions from former-insiders, academics, and campaigners for justice, The Spider's Web reveals how, in the world of international finance, corruption and secrecy have prevailed over regulation and transparency, and how the United Kingdom is a pioneer of the modern corrupt global economy.
Over the past three decades, obesity rates in the United States have more than doubled for children and tripled for adolescents, and a startling 70% of adults are now obese or overweight. The result has been a widening epidemic of obesity-related health problems. But while discussions about this crisis tend to focus solely on the need for individual responsibility and more exercise, Feeding Frenzy turns its focus squarely on the responsibility of the processed food industry and the outmoded government policies it benefits from. It lays bare how government subsidies designed to feed the hungry during the Great Depression have enabled the food industry to flood the market with a rising tide of cheap, addictive, high calorie food products, and offers an engrossing look at the tactics of the multi billion-dollar advertising industry that makes sure that everyone keeps consuming.
Skandal!
Skandal! Bringing Down Wirecard is a thriller documentary of one of the largest world-wide financial crimes. It follows journalist Dan McCrum, who reveals the inside story of a 6-year investigation into the German corporation Wirecard and the dirty tricks that were deployed against him and the Financial Times, as they battle to expose a multi-billion euro fraud at the centre of one of Germany's most successful online payment corporations of the time. The film traverses the colourful characters of the scam, such as the mafia, porn barons, gambling outfits, Libyan and Russian intelligence agencies, corporate spies, private investigators, hired thugs and surveillance operatives, demanding answers of the chief executive officer, Markus Braun, awaiting trial in Munich, and its mysterious chief operating officer, Jan Marsalek, who vanishes.
Confessions of an Economic Hit Man is a presentation by John Perkins, based on the book by the same name published by him in 2004. Perkins describes the role: "Economic hit men are highly-paid professionals who cheat countries around the globe out of trillions of dollars. They funnel money from the World Bank, the US Agency for International Development (USAID), and other foreign "aid" organisations into the coffers of huge corporations and the pockets of a few wealthy families who control the planet's natural resources. Their tools included fraudulent financial reports, rigged elections, pay-offs, extortion, sex, and murder. They play a game as old as empire, but one that has taken on new and terrifying dimensions during this time of globalisation."
Generation Wealth is a visual history of the materialistic, image, and celebrity-obsessed culture, explored through the work of photographer and filmmaker Lauren Greenfield. Part historical essay, part autobiographical, Greenfield puts the pieces of her life's work together to reveal the pathologies that have created the richest and most unequal society the world has ever seen. Spanning consumerism, beauty, gender, body commodification, aging, and sex, Generation Wealth unpacks the global boom-bust economy, the corrupt American Dream and the human costs of capitalism, narcissism and greed.
Sweet Crude
Sweet Crude is the story of how large oil corporations such as Shell and Chevron have absolutely decimated the Niger Delta, but the people are fighting back. The film shows the human and environmental consequences of 50 years of oil extraction against an insurgency of people who, in the three years after the filmmakers met them as college students, became the young of the Movement for the Emancipation of the Niger Delta (MEND). The movement is born after series of non-violent protests, and what the corporations and colonisers don't understand is that these people will fight for their land and emancipation until the end. Sweet Crude is their story of survival and armed resistance against corrupt governments and rapacious corporate power, amongst a complicit and collusive mainstream media.
2009, pornography has grown into a $10 billion business, and some of the world's most-known corporations are silently sharing in the profits. Companies like Time Warner, Marriott, and Vodaphone earn huge amounts of revenue by piping pornography into homes and hotel rooms, but you won't see anything about it in their company reports. Even the Catholic Church invests in companies that distribute pornography, along with pension funds that earn huge profits from investing in ventures that relate to porn. Hardcore Profits is a two part television series that explores how in the 21st century, pornography has never been more profitable, nor more pervasive.
The True Cost is a global investigation into the clothes we wear, the people who make them, and the impact the industry is having on the world. The price of clothing has been decreasing for decades, while the human and environmental costs have grown catastrophically. The True Cost pulls back the curtain on the untold story and asks us to consider, who really pays the price for our clothing?
Robert Kenner and Melissa Robledo team up with authors Michael Pollan and Eric Schlosser to examine the modern food industry's efficiency and vulnerabilities as a follow-up to the first documentary of the same title. This film focuses on corporate consolidation in the food and agriculture business in the United States, while raising questions about the future of the industrial food system.
Let's Make Money investigates the development of the world-wide financial system, showing that elitists economically exploit the rest of society, especially in the developing world, but also in western nations. Using the savings of a typical depositor as a case study, the film moves around the global system, showing exploitation at many levels. There are several interviews with investment managers, politicians, economists as well as homeless people and workers who give their take on the system and its impacts...