Ten years on from his previous film, Advertising & the End of the World, renowned media scholar Sut Jhally follows up by exploring the since-escalating devastating personal and environmental fallouts of advertising and the near-totalising commercial culture. The film tracks the emergence of the advertising industry in the early 20th century to the full-scale commercialisation of the culture today, identifying the myth running throughout all of advertising: the idea that corporate brands and consumer goods are the keys to human happiness and fulfilment. We see how this powerful narrative, backed by billions of dollars a year and propagated by clever manipulative minds, has blinded us to the catastrophic costs of ever-accelerating rates of consumption. The result is a powerful film that unpacks fundamental issues surrounding commercialism, media culture, social well-being, environmental degradation, and the dichotomy between capitalism and democracy.
Filmmaker Darryl Roberts goes on a five year journey to examine this culture's burgeoning obsession with physical beauty and perfection, showing how increasingly unattainable images contribute to the rise in low self-esteem, body dismorphia, and eating disorders for young women and girls who also happen to be the beauty industry's largest consumers. In almost 40,000 media messages a year, young people are being told that unless you look like supermodels and rock stars, you're not good enough for anyone. In 2004 alone, people across the United States spent $12.4 billion on cosmetic surgery. America the Beautiful explores why these people are spending so much money to cover up their discontent that is mainly driven by advertising. What are the true costs of this culture's obsession with youth, plastic notions of beauty, and impossibly slender physiques? Who actually benefits from this high-priced journey towards a fake ideal, and does it justify an entire nation's psychosis?
How do our families influence our relationship with our own bodies? How does popular culture's standards of beauty get inside our hearts and heads? In what ways can sport and the drive for fitness actually make us sick rather than healthy? In Beauty Mark, former champion triathlete Diane Israel examines this culture's unhealthy fixation on thinness, beauty, and physical perfection. She talks candidly about her own struggle with eating disorders and obsessive exercising, confronting her own past to come to terms with this culture's unhealthy fixation on self-destructive ideals of beauty and competitiveness.
Fuelled by popular personalities on Instagram, YouTube and Snapchat, cosmetic surgery is pushing further into the mainstream. Huge numbers of people, predominantly young women, are choosing to alter their appearance forever as though it's as simple as buying a new set of clothes. Social-media "influencers" get free procedures in exchange for promoting certain doctors or agencies or products to their audiences. Going on the numbers alone, audiences seem to respond to this blatantly cacophonous advertising, following their social media stars closely, and taking out huge personal loans to get surgery and "keep up with the Kardashians." Doctors offering the surgery are even becoming media stars themselves, and it's redefining the meaning of doctor/patient relations. Underpinning this entire industry, is a business model of targeting women who can barely afford procedures by selling the dream of a "new you." Social-media laps it up, and the cycle repeats. But as this investigation shows, when things go wrong, the physical and financial costs are devastating. Real doctors who are left to pick up the pieces, are warning that the booming industry is creating a dangerous legacy, and not just to the concept of beauty.
What do popular television programs like What Not to Wear, The Biggest Loser, Queer Eye for the Straight Guy, and The Swan tell us about how to look and feel? What do they tell us about what a good life is supposed to look like? Brand New You explores these questions, and also asks what it means to be an authentic self in an extensively mediated world. It shows how the interventions featured in makeover shows—from weight loss to cosmetic surgery to rearing competitiveness—create, perpetuate and reproduce conventional norms of physical attractiveness and success. By taking a wider social and cultural view, Brand New You also shows how these programs have become tools of rampant individualism, consumerism and inner self-transformation at precisely the same time that collective awareness of social issues has dissipated.
Can't Get You Out of My Head: An Emotional History of the Modern World is a six-part series that explores how modern society has arrived to the strange place it is today. The series traverses themes of love, power, money, corruption, the ghosts of empire, the history of China, opium and opioids, the strange roots of modern conspiracy theories, and the history of Artificial Intelligence and surveillance. The series deals with the rise of individualism and populism throughout history, and the failures of a wide range of resistance movements throughout time and various countries, pointing to how revolution has been subsumed in various ways by spectacle and culture, because of the way power has been forgotten or given away.
Diamond Empire is a two-part series that investigates how an advertising slogan invented by Madison Avenue executives in 1948 has come to define some of the most intimate and romantic rituals and ideals of this culture. The films take apart the myth that "diamonds are forever," exposing how one white South African family, through a process of monopoly and fantasy, managed to exert control over the global flow of diamonds and change the very way this culture projects the notion of courtship, marriage, and love--an achievement all the more stunning given that diamonds are in fact neither scarce nor imperishable. Zeroing in on how the diamond empire managed to convert something valueless into one of the most coveted commodities in history, these films provide a vigorous investigation into how marketing and consumer culture shape not only global trade and economics, but also our very identities.
Facing Beauty
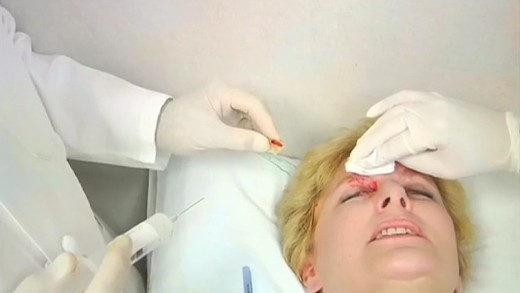
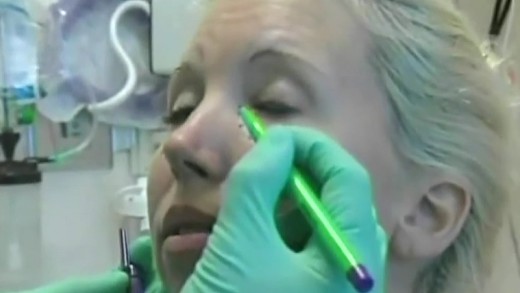
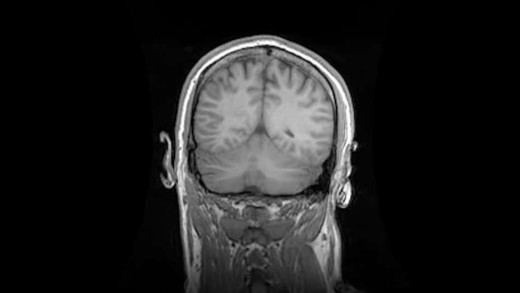
Facing Beauty examines the explosive growth of the plastic surgery industry, by looking through China's beauty obsession and the social media influencers that are driving its mindset. A mobile app has captured the population by promoting an "ideal ratio in human facial features," where users' faces are assessed and given a score. The app then draws up plans for surgeries to lower that score, referring users to endorsed clinics, driving both non-invasive and invasive surgeries and procedures. Now, demand for those procedures is so widespread among the country's youth population, it's estimated the industry will be worth US$200 billion by 2030. This growth in the industry has led to an expansion of 'beauty' institutions that employ staff without adequate medical qualifications or protections, and even though some procedures have been banned and the negative health impacts shown, demand continues to increase at fever pitch.
Generation M looks at misogyny and sexism in mainstream media, exploring how negative definitions of femininity and hateful attitudes toward women get constructed and perpetuated throughout popular culture. The film tracks this across a broad and disturbing range of media phenomena: from the hyper-sexualization of commercial products aimed at girls, to the explosion of violence against women in video games aimed at boys; from the hysterical sexist rants of popular hip-hop artists and talk-radio shock-jocks, to the continually harsh, patronizing caricature of women found in virtually every area of media. Generation M posits the consequences of misogyny in all of its forms, showing that when we devalue more than half the population based on gender, we harm everyone—boys and men, women and girls alike.
Generation Wealth is a visual history of the materialistic, image, and celebrity-obsessed culture, explored through the work of photographer and filmmaker Lauren Greenfield. Part historical essay, part autobiographical, Greenfield puts the pieces of her life's work together to reveal the pathologies that have created the richest and most unequal society the world has ever seen. Spanning consumerism, beauty, gender, body commodification, aging, and sex, Generation Wealth unpacks the global boom-bust economy, the corrupt American Dream and the human costs of capitalism, narcissism and greed.
Girl Model offers a glimpse into the hall of mirrors that is the modelling world as it interfaces with other industries and other countries. The film follows Ashley—a deeply ambivalent former-model who is now a scout and scours the Siberian countryside looking for 'fresh faces' to send to the Japanese market; and one of her 'discoveries,' Nadya, a thirteen year-old plucked from the Siberian countryside and dropped into the centre of Tokyo with promises of a profitable career. What entails is the opening of a can of worms that isn't easily solved in one sitting—a thriving and curiously sinister modelling industry that spans the globe, luring everywhere with pretences of wonder, success and riches. But the realities are harsh. The fashion industry can look glamorous from the outside, but its insides are, at the very least, deceptive and sinister; and the myths run deeply entrenched in the culture, constantly promulgating new, young recruits. This 'meat market,' a prelude to sex trafficking, is creepy, ugly, and preys on the young and vulnerable. Can the spell be broken?
Going Clear
Going Clear: Scientology and the Prison of Belief profiles eight former-members of the cult of Scientology, leading to a series of revelations of the history of systematic abuse, manipulation, and betrayal in the organisation by Scientology officials and celebrity figures. The film highlights the origins of Scientology, from its roots in the mind of founder L. Ron Hubbard and successor David Miscavige, to its rise in popularity in Hollywood and beyond. The result is a record of great harm, paranoia, abuse, the vast accumulation of wealth, and a lust for power and control.
High Tech, Low Life follows the journey of two Chinese bloggers who travel their country chronicling undner-reported news and social issues stories. Using laptops, mobile phones, and digital cameras, both develop skills for reporting while learning to navigate China's continually evolving censorship regime and the risks of political persecution. The film follows 57-year-old 'Tiger Temple,' who earns the title of China's first "citizen reporter" after he impulsively documents an unfolding murder; and 27-year-old 'Zola' who recognises the opportunity to be famous by reporting on sensitive news throughout China. From the perspective of vastly different generations, both personalities must reconcile an evolving sense of individualism, social responsibility and personal sacrifice. The juxtaposition of Zola's coming-of-age journey from veggie-farmer to Internet celebrity; and Tiger Temple's commitment to understanding China's tumultuous past, both provide a portrait of China and of the wider questions facing news-reporting in the age of the Internet.
Instafame is an exploration of a teenager's relationship with the concepts of success and fame through the lens of the screen, exemplified by the popular photo-sharing website 'Instagram.' The short film speaks volumes about this specific aspect of screen culture in that the notions of celebrity are self-reinforced in the closed-loop of the 'social networking' environment which is itself a purpose-built, commercially-mediated experience. So what happens to the notions of identity, friendship, personality and so on; in this space, and in the wider culture?
We've been told again and again that sports and politics don't mix, that games are just games and athletes should just "shut up and play." But Not Just a Game argues that far from providing merely escapist entertainment, American sports have long been at the centre of some of the major political debates and struggles of our time. By tracing the good, the bad, and the ugly of American sports culture, Not Just a Game shows how American sports have glamorised militarism, racism, sexism, and homophobia; but also traces a largely forgotten history of rebel athletes who stood up to power and fought for social justice beyond the field of play.
Pornland
Pornography has moved from the outskirts of society into the very mainstream of this culture in over less than a span of a generation. From MTV to Internet pornography everywhere, pop culture industries continue to bombard all of us with sexualised images of idealised women and men that jump off the screen and go straight into our lives, profoundly shaping our identity, the ideas and acceptability of body image, and our most intimate relationships. In this video essay, based on the book of the same name, leading scholar and activist Gail Dines argues that the dominant images and stories disseminated by the porn industry, produce and reproduce a system that perpetuates social inequality and encourages violence against women at its very core. In direct opposition to the claims that pornography has delivered a more liberated, equitable and edgy sexuality, Pornland reveals a mass-produced vision of sex that is profoundly sexist, destructive and pervasive in this culture—a world that severely limits and undermines our collective ability to live authentic, truly equal relationships, free of systemic violence and degradation.
Everybody who has survived adolescence knows what a scary, tumultuous, exciting time it is. But if we use memories of our experiences to guide our understanding of what today's girls are living through, we make a serious mistake. Girls are living in a new world. Reviving Ophelia is a call from Dr. Mary Pipher, a psychologist who has worked with teenagers for more than a decade. She finds that in spite of the women's movement, which has empowered adult women in some ways, teenage girls today are having a harder time than ever before because of higher levels of violence and sexism in the culture. The current crises of adolescence--frequent suicide attempts, dropping out of school and running away from home, teenage pregnancies in unprecedented numbers, and an epidemic of eating disorders--are caused not so much by "dysfunctional families" or incorrect messages from parents as by our media-saturated, image-obsessed culture.
Risk
Cornered in the tiny building of the Ecuadorian embassy in the United Kingdom for half a decade, WikiLeaks founder Julian Assange and his team are undeterred, continuing to release troves of important documents, even as the personal legal jeopardy he faces threatens to undermine the very organisation he leads and fracture the movement it inspired. Filmmaker Laura Poitras finds herself caught between the motives and contradictions of Assange and his inner circle. Filmed over six years, Risk is a complex and volatile character study of the forces that crescendo with a high-stakes election year in the United States and its controversial aftermath. In a world order where a single keystroke can alter history, Risk is a nuanced and curious portrait of power, betrayal, truth, and sacrifice. How much of your own life are you willing to risk?
Sexy Baby
An ex-pornstar, a 12 year old girl, and a 22 year old who yearns for the 'normal' genitals as seen in porn movies, are just some of whom are chronicled in Sexy Baby to draw together how the current relentless culture of pornography, social media and popular culture are deeply and profoundly affecting the lives women and girls. Based on intimate and candid conversations with kids in middle school classrooms, suburban shopping malls, nightclubs, college dorms, and high school house parties, the film chronicles trends among small town and big city kids--the pervasive culture affects everyone, everywhere. Most youngsters know someone who has emailed or texted a naked photo of themselves. Many kids have accidentally or intentionally had their first introduction to sex be via hardcore pornography online. Facebook has created an arena where kids compete to be "liked" and constantly worry about what image to portray. Much of what was once private is now made public. The list goes on. Sexy Baby is a powerful indictment of the Internet age and the hyper-sexualised culture affecting women and girls everywhere, as well as an insight into the struggle of parents navigating this new culture, wanting what is best for their kids and the generations to come.
Shifty
Shifty is a series of films that traverse the past 40 years in Britain, showing how the shift of political power to finance and hyper-individualism came together in powerful ways, to undermine one of the fundamental structures of mass democracy--the shared idea of what is real. As that fell apart, with it went the language and the ideas that people had turned to for the last 150 years to make sense of the world they lived in. As a result, life in Britain and the current and former colonies of its empire, has become strange--a hazy dream-like flux, where distrust in politicians keeps growing, and the political class seems to have lost control. Through archive footage, news reels, and on-screen-text in video essay format, Shifty documents the shapes of how this happened, using the vast ranges of footage to evoke what if felt like to live through an epic transformation during the 1980s.
Spin the Bottle critiques the role that popular culture plays in glamorising excessive drinking and high-risk behaviour, in contrast to the ways alcohol affects the lives of real young men and women in reality. This film decodes the power and influence of seductive media images to show how they shape personal identity when linked to the use of alcohol. Nowhere is this link more apparent than on America's college campuses. By exploring the party scene, Spin the Bottle also shows the difficulties young people have in navigating a cultural environment saturated with messages about gender and alcohol. Interviews with health professionals provide a clear picture of how drinking impacts student health and academic performance, but it is the students' own experiences and reflections that tell the real story behind alcohol's alluring public and cultural image.
Starsuckers
By planting a variety of fake celebrity-related stories in the UK media and having tabloid newspapers accept them without corroboration or evidence, Starsuckers navigates through the shams and deceit involved in creating a pernicious celebrity culture, uncovering the real reasons behind the addiction to fame and the corporations and individuals who profit from it.
Steve Jobs: The Man in the Machine is not just another celebratory biographical film about the life of a business man that many around the world grieved in 2011. It's a full rounded critical examination into the fundamentals of a person revered as an iconoclast, a barbed-tongued tyrant, a business sociopath. The real Steve Jobs is revealed like this through candid interviews from those who had close relationships with him at different stages of his life, including the mother of his child, Lisa, that Jobs refused he had, but named a computer after instead. The film also takes us through the evocative essence of the brand of Apple Computers which has captured the population like zombies, and asks the question: What is the legacy of this industry, and the truth of this kind of person that the culture celebrates so much, completely ignoring the darkness?
This film examines the forces of culture influencing young people's decisions about sex: media, family, religion, alcohol, and so on. By examining the cultural environment in this way, this film becomes a tool for facilitating informed discussions about the myriad influences facing young people. Filmmaker Dan Habib features the stories of eight young people, ages 16-24, and weaves them with observations about the messages young people get from popular culture.
The Bro Code unpacks and takes aim at the forces of masculinity that condition boys and men to fundamentally dehumanise and disrespect women. The film breaks down a range of contemporary media forms that are saturated with sexism—movies and music videos that glamorise misogyny, pornography that trades in the brutalisation and commodification of women, comedy routines that make light of sexual assault, and a slate of men's magazines and TV shows that propagate myths of what it means to be a man in this culture: that it's not only normal, but "cool" for boys and men to control and humiliate women. There's nothing natural or inevitable about this mentality. And it's extremely harmful in the real world. By setting the myths against reality, The Bro Code challenges young people to step up and fight back against this culture, to reject the fundamental idea that being a 'real man' means disrespecting women.
The Empathy Gap investigates how dominant culture bombards young men with sexist and misogynistic messages and argues that these messages not only devalue women but also undercut men's innate capacity for caring and empathy. The film looks closely at the ways these messages short-circuit men's ability to empathize with women, respect them as equals, and take feminism seriously, drawing parallels between sexism and racism, spelling out how each is rooted in cultural norms that discourage empathy, and shows how men who break with these norms live happier and healthier lives.
By examining the people and practices of the media and entertainment industries, The Fourth Estate illuminates not only specific incidences of corruption by press groups, but how the wider model of mainstream journalism itself as a for-profit entity has a huge amount to answer for in terms of democracy and the state of politics throughout the world. Filmed over two years throughout the UK on no budget, the filmmakers profile journalists, organisers and critics of industrial media practices, stemming from the Leveson Inquiry in 2011 which was set up to examine the culture, practices and ethics of the British press following the News International phone hacking scandals of the Murdoch media empire. While the phone hacking scandal illuminated the depth and breadth of the culture of British journalism, the media's focus at the time quickly diverted from a brief period of self-examination, back to business as usual. This film instead continues the analysis by looking at the larger implications of a for-profit media model and its connections to ideology, entertainment, and hence the resulting political framework that's in crisis.
The Illusionists examines how global advertising firms, mass media, and the beauty, fashion, and cosmetic-surgery industries have together colonised the way people all around the world define beauty and see themselves. Taking us from Harvard to the halls of the Louvre, from a cosmetic surgeon's office in Beirut to the heart of Tokyo's Electric Town, The Illusionists shows how these industries saturate our lives with narrow, Westernised, consumer-driven images of so-called beauty that show little to no respect for biological realities or cultural differences. Featuring voices from prominent sociologists, magazine editors, scientists, artists, and activists, The Illusionists documents a truly global phenomenon, with hegemonic results.