The Carlyle Group is one of the largest investment banks in the world. Based in Washington, it has accumulated its wealth mainly by investments in defence--a lucrative market in the continued tradition of American war, imperialism and militarism. A strange coincidence? Their list of private investors include George Soros, the Saudi Royal Family and the Bin Laden Family. How does the Carlyle Group really operate and who are the people behind it?
No Logo
In the age of the brand, logos are everywhere. But why do some of the world's best-known brands find themselves at the end of spray paint cans and the targets of anti-corporate campaigns? No Logo, based on the best-selling book by Canadian journalist and activist Naomi Klein, reveals the reasons behind the backlash against the increasing economic and cultural reach of multinational companies. Analysing how brands like Nike, The Gap, and Tommy Hilfiger became revered symbols worldwide, Klein argues that globalisation is a process whereby corporations discovered that profits lay not in making products (outsourced to low-wage workers in developing countries), but in creating branded identities people adopt in their lifestyles. Using hundreds of media examples, No Logo shows how the commercial takeover of public space, the restriction of 'choice', and replacement of real jobs with temporary work -- the dynamics of corporate globalisation -- impact everyone, everywhere...
The Medicated Child confronts psychiatrists, researchers and government regulators about the risks, benefits and many questions surrounding psychotropic drugs for children. The biggest current controversy surrounds the diagnosis of bipolar disorder. Formerly called manic depression, bipolar disorder was long believed to only 'apply to adults', but in the mid-1990s 'bipolar disorder in children' began to be diagnosed at much higher rates, sometimes in children as young as 4 years old...
Across the globe, this culture is polluting, diverting, pumping and wasting fresh water at a crazy rate, as population grows and technology escalates. The rampant expansion of agriculture, housing and industry increase the demands for fresh water well beyond the limited supply, resulting in the desertification of the Earth. Corporate giants force developing countries to privatise their water supply for profit, Wall Street investors target desalination and mass bulk-water export schemes, while governments use water for economic and political gain. Military control of water emerges and a new geo-political map and power structure forms, setting the stage for global conflict over fresh water. Blue Gold follows numerous worldwide examples of people fighting for their basic right to water, from court cases to United Nations conventions, to revised constitutions, to local protests at grade schools, to complete revolutions. A line is crossed when water is a commodity. Will you fight to stop it and protect it?
Cypherpunks is a movement originating from the 1980s aiming to improve Internet privacy and security through proactive use of cryptography. With WikiLeaks being a recent offshoot of the many projects derived from the Cypherpunk movement, WikiLeaks editor Julian Assange talks with three activists from the Cyberpunk world to cover the topics of mass surveillance and social control being tied directly into technology as modern society progressively intertwines with technological progress...
Advances in technology, global demand and the very essence of the commercial fishing industry itself means that whole species of wild fish are under threat. The species of fish that we eat today are predicted to be in a state of collapse by 2050 -- some are already extinct. Overfishing, or even more simply, the commercial fishing industry in general is to blame for this, along with celebrity chefs and 'exotic' restaurants; and mass consumer demand in today's world of globalisation. The End Of The Line documents the concerns and the processes behind commercial fishing and it's impact on the environment, the climate and the future existence of many species -- including our own...
Admit it--you don't really read the endless pages of terms and conditions connected to every website you visit or phone call that you make do you? Of course not. But every day billion-dollar corporations are learning more about your interests, your friends and family, your finances, and your secrets--precisely because of this; and are not only selling the information to the highest bidder, but freely sharing it with the government. And you agreed to all of it. With plenty of recent real-world examples, Terms And Conditions May Apply covers just a little of what governments and corporations are legally taking from Internet users every day--turning the future of both privacy and civil liberties into serious question. From whistleblowers and investigative journalists to zombie fan clubs and Egyptian dissidents, this film demonstrates how all of us online have incrementally opted-in to a real-time surveillance state, click by click.
From its extraction through sale, use and disposal, all the stuff in our lives affects communities at home and abroad, yet most of this is hidden from view. This is by design. The Story of Stuff serves as an introduction to the underside of the current world of mass production and consumption, exposing the connections between a huge number of environmental and social issues -- shedding the light on the hidden processes behind our modern world. How can we create a more sustainable and just economy?
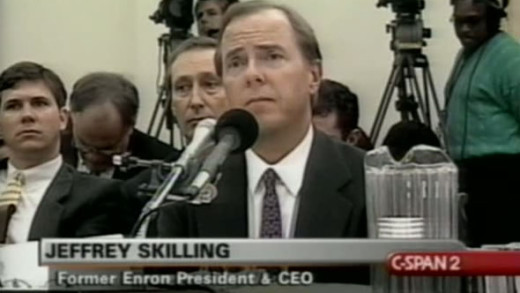
In 2001, the collapse of the Enron Corporation was of one of the largest business scandals in American history. The collapse resulted in criminal trials for several of the company's top executives, bringing the facts of exposure to Enron's involvement in the California electricity "crisis," where the company had rigged the market in order to generate huge speculative profits during the power shortages and blackouts of the time that effected millions of people.
The Dark Side Of Chocolate follows a team of investigative reporters into Africa where human trafficking and child labour fuel the chocolate industry worldwide. The film travels to Mali where hidden footage reveals the trafficking of small children to the cocoa fields in the neighbouring Ivory Coast and elsewhere. What is happening behind the sweet imagery of the chocolate industry?
There is an staunch connection between medical science, the pharmaceutical industry and the structures of modern society. Drug manufacturers today fund aggressive marketing campaigns designed to create public awareness of "previously unknown diseases," or conditions known by less dramatic names in order to sell pharmaceutical drugs and other psychotropic interventions. Shyness is thus marketed as "Social Anxiety Disorder," worry becomes "Generalised Anxiety," and premenstrual tension as "Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder" which must be treated by drugs made popular through advertising, such as Paxil, Zoloft and Prozac. These drugs have become household names, not to mention a 20 billion dollar a year racket. How? Why?
The Secret of the Seven Sisters is a four-part series examining the rise of a powerful cartel of seven companies that control the world's oil supply. The 'seven sisters' comprises Anglo-Persian Oil Company (now BP); Gulf Oil, Standard Oil of California (SoCal) and Texaco (now Chevron); Royal Dutch Shell; Standard Oil of New Jersey (Esso) and Standard Oil Company of New York (Socony), (now ExxonMobil). Prior to the oil crisis of 1973, the Seven Sisters controlled around 85% of the world's petroleum reserves, but in recent decades the dominance of the companies and their successors has declined. This series is about the power of oil, the conspiracy of business, and the control that oil provides the few...
The Garden
The Garden tells the story of South Central Farm -- a 14 acre community garden and urban farm located in Los Angeles, California, which was in operation between 1994 and 2006. The entire lot is evicted and demolished against overwhelming local support for the farm and also despite the community raising an incredible amount of money to purchase the land from the owner. The owner refuses to sell and the land is demolished and still sits vacant, unused...
The Future of Food brings together the many complex issues surrounding the troubling changes that have occurred in the industrial food system during the past decades—genetically modified food, seed patenting, pesticides; and the corporate takeover of the entire food chain, from soil to seed to fork. The issues raised in The Future of Food are more pressing than ever, as the collusion between governments and large multi-national corporations is more visibly on display than ever before—the use and abuse of the legal system, politicking, and privatisation drive this rapacious strangle hold on much of the world's food. The film focuses on unlabelled, patented, genetically engineered foods that have been sold in supermarkets in the United States, unbeknownst to the public, for the past decade. In addition, there is a focus on Canada and Mexico. Also described is the concern about 'terminator' GMO seeds that pose a huge threat to diversity and local food systems. Genetically modified food is as controversial today as ever, and The Future of Food presents a vital educational tool for activists and educators worldwide.
Dirty Money
In the late 1990s, the Reserve Bank of Australia thought it was on a winner. The bank had developed the technology to create polymer bank notes that it claimed rivalled paper money. So the Reserve Bank decided to set up a subsidiary company called Securency to sell the technology to the world. It had just one problem though—getting legitimate access to other central bank officials to pitch the idea. So instead, Securency decided to employ a shadow network of local "fixer agents" to make "connections" with relevant officials, lavishing them with prostitutes, cash, and bribing them into deals. Dirty Money is the story of this institutional corruption at the highest level of finance in Australia.
On April 22, 2010 the Deepwater Horizon offshore drilling rig, run by oil giant BP, sunk into the Gulf of Mexico--creating the world's biggest and most catastrophic environmental crime in history. After over 750 million litres of crude oil and millions of litres of the chemical dispersant Corexit dumped into the sea, the disaster was deemed over and all damage repaired. This is bullshit however. Film-makers Josh and Rebecca Tickell travel to the Gulf of Mexico to document first-hand the extent of environmental and community damage, continuing many years after the explosion. Beginning by tracing BP’s origins and fingerprints across decades of US manipulation in Iran, The Big Fix assembles an indictment of this monumental disaster by unpacking the workings of the complex oligarchies that put pursuit of profit over all other ends...
Two film students set out to explore the psychological and manipulative powers of consumerism by creating an extensive and pervasive advertising campaign for a fake hypermarket. The ads appear on radio, television, billboards; there is a promotional song, an internet site, ads in newspapers, magazines, and flyers with photos of fake Czech Dream products are distributed. Will people believe it and show up for the grand opening?
Coca Cola is one of the most visible brands in the world, but there's one part of the operations the corporation doesn't want you to see. Colombia is the trade-union-murder-capital of the world. Since 2002, more than 470 workers' leaders have been brutally killed, usually by paramilitaries hired by private companies intent on crushing the unions. Amongst the top unscrupulous corporate brands is Coca Cola...
Recorded by over 100 media activists, this film tells the story of the enormous street protests in Seattle, Washington in November 1999, against the World Trade Organisation summit. Vowing to oppose--among other faults--the WTO's power to arbitrarily overrule nations' environmental, social and labour policies in favour of unbridled corporate greed, thousands of people from all around the United States came out in force to stop the summit. Against them was a brutal police force and a hostile media. This Is What Democracy Looks Like documents the struggle, as well as providing a narrative to the history of success and failure of modern political resistance movements.
Flow—For The Love Of Water builds a case against the growing privatisation of the world's dwindling fresh water supply with a specific focus on human rights, pollution, the politic of corporate influence in the emergence of a domineering global water cartel. The film names and clearly documents many of the culprits, while asking the question—can anyone really 'own' water?
Filmed over three years, Hacking Democracy documents a group of American citizens investigating anomalies and irregularities with the electronic voting systems used during the 2000 and 2004 US Presidential elections. The investigation revolves around the flawed integrity and security of the machines, particularly those made by the Diebold corporation. Could the elections have been rigged?
h2Oil
Canada is now the biggest supplier of oil to the United States, thanks to the Alberta tar sands—a controversial billion-dollar project to extract crude oil from bitumen sands, using a very toxic process that has generated international cause for concern. Four barrels of glacier-fed spring water are used to process each barrel of oil, along with vast amounts of electricity. The waste water is dumped, filled with carcinogens and other chemicals, into leaky tailings ponds so huge that the piles can be seen from space. Downstream, people and communities are already paying the price with contaminated water supplies and clusters of rare cancers. Evidence mounts for industry and government cover-ups. In a time when wars are fought over dwindling oil and a crisis looms over access to fresh water, which will we allow to turn out to be more precious to us?
The Biotech Revolution is largely an exploration by scientists working in genetics and biotechnology that repeatedly promise "unprecedented health benefits and longevity for all," amongst other things, to rationalise their work in the so-called "biotechnology revolution." But in reality, isn't this "revolution" simply just more of the same control imperative of science and this culture's technology, essentially ending in the prospect of a monoculture of genetically modified people? Will such control foster into globalisation a history of inclusion and harmony? Or, will we simply end up in an extension of the current order, albeit one that is further divided, this time by genetic apartheid?
Every day, escalating technologies are being used to monitor all of us as populations with unprecedented scrutiny—from driving habits to workplace surveillance, as shoppers, as consumers, as citizens. We are all increasingly being observed and analysed. Internet searches are monitored and used as evidence in court, the police track our movements on the road, governments collect our DNA, fingerprints and iris scans, corporations assemble huge databases for profiling and selling data, while governments collude with such lucrative businesses—for example, Acxiom, Lexis Nexis and ChoicePoint—to gain access to vast volumes of information about people and the machinations of modern society. What will it take for us to stop this system before it boils over into a full-blown technocratic authoritarian regime?
They spend their days sifting through reams of market research data. They conduct endless surveys and focus groups. They comb the streets, the schools and the malls, hot on the trail of the "next big thing" that will snare the attention of their prey -- a market segment worth an estimated $150 billion a year. They are the merchants of cool: creators and sellers of 'popular culture' who have made teenagers the hottest consumer demographic...
From the front-lines of conflicts in Mexico, Argentina, South Africa, Palestine, Korea, and the North; from Seattle to Genova and the "War on Terror" in New York, Afghanistan, and Iraq, The Fourth World War documents the stories of women and men all around the world who resist being annihilated in this war. Centred around economics and systems such as NAFTA, GATT, the G20, APEC and others, this is a war which plays along with the spread of rapacious globalisation, a feat that has pervasive consequences in the real world...
Pepsi vs. Coke in The Ice Cold War traces the history of the worldwide struggle for soft drink supremacy by the Coca Cola Company, against the backdrop of World War II. The war was the perfect vehicle for Coca-Cola distribution, including to the Nazis. Bottling plants on front lines were paid for by the US war department. Nixon got Kremlin supremo, Khrushchev, to pose drinking Pepsi, which became the first US product made in the Soviet Union. In 1949, Mao kicked Coca-Cola out of China. President Carter got it back in 1978. In Chile, Pepsi Cola's boss ran a daily paper which was used by the CIA to help Pinochet's bloody coup...
Corporations On Trial is a five-part series following just some of the many lawsuits being brought against multinational corporations for war crimes, conspiracy, corruption, assassinations, environmental devastation and payments to terrorists. Such serious charges have forced some of the world's largest companies to hire high-profile defence lawyers to protect public relations in cases often brought by plaintiffs who are barely literate. These five films reveal a growing anxiety about the power and influence of big business, as many multinational corporations have annual revenues greater than some countries' national budgets and indeed increasingly hold governments to ransom by their economic power. Around the world, ordinary people are fighting back and asking how many more times their interests should be sacrificed for corporate greed and shareholder profit...