Project X is a short film taking viewers on an undercover journey based on formerly top-secret documents that show a partnership between the National Security Agency and telecommunications corporations such as AT&T and Verizon for mass surveillance and bulk data collection of voice and data. The documents reveal TITANPOINTE, the codename for a large windowless sky scraper in New York, where AT&T and other corporations house vast Internet switching equipment and data centres. The facility is also tied to a nearby FBI building, and its rooftop equipment to the SKIDROWE satellite surveillance system. These findings were possible because of documents released to the public by Edward Snowden and other brave whistleblowers.
MLK/FBI documents the extent of the FBI's surveillance and harassment of Martin Luther King based on newly declassified files and documents obtained through the Freedom of Information Act and unsealed by the National Archives. Using these, as well as restored historical video footage, the film explores the United States government's history of targeting Black activists through surveillance programs specifically aimed the Civil Rights Movement. The film covers the attempts by J. Edgar Hoover and the FBI to personally discredit King by collecting recordings and images of his private sexual life with women other than his wife. This was used to denigrate his status within the civil rights movement in the United States. Not all FBI documents have been declassified, but the whole record will be made available public in 2027.
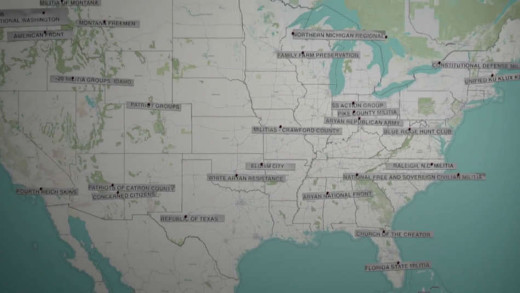
Shortly before dawn on August 21, 1992, United States Marshals initiated actions to apprehend and arrest Randy Weaver, a former US Army engineer, when he failed to appear in court on firearms charges after being coaxed by undercover agents to sell them sawed-off shotguns after hanging out with nazis and white supremacists. Given three conflicting dates for his court appearance, and suspecting a conspiracy against him, Weaver refused to surrender, and members of his immediate family and family friend Kevin Harris resisted as well, isolating themselves in their mountaintop home in Ruby Ridge, Idaho. When federal agents surveilling the property got close to members of the family, they also initiated a gunfight that mesmerised the nation, leaving Weaver injured, his son killed, and Striker the family dog dead. In the subsequent siege led by the FBI, Weaver's wife Vicki was also killed, while holding her baby, by a shot in the head from a FBI sniper. Drawing upon eyewitness accounts, including interviews with Weaver's daughter, Sara, and federal agents involved in the confrontation, Ruby Ridge is an overview of a tragic catalysing event that helped fuel conspiracy theories and give rise to the modern American militia movement.
(T)error is the story of a 62-year-old Theodore Shelby, a former Black Panther now turned informant for the FBI going under the name Saeed “Shariff” Torres. The film documents his work on an undercover sting operation that targets a Muslim American Khalifah Ali Al-Akili on weapons charges, as well as Tarik Shah, a professional jazz musician, accused of providing support to al-Qaeda, even though no actual terrorist contact ever took place. The cases are used as examples of preemptive prosecutions, and illuminate aspects of the surveillance state in the post-9/11 world of the United States.
Through a secret program called the Counter Intelligence Program or 'COINTELPRO', the United States government set out to "disrupt dissident political organisations using infiltration, psychological warfare, harassment through the legal system and extralegal force and violence". Groups such as the Black Panther Party and others throughout the civil rights movement were targets of the program. COINTELPRO -- The FBI's War On Black America establishes a historical perspective on the measures initiated by the FBI which aimed to discredit black political figures and forces of the late 1960s and early 1970s. Combining declassified documents, interviews, rare footage and exhaustive research, it investigates the government's role in the assassinations of Malcolm X, Fred Hampton, and Martin Luther King...
In the Arab-American neighbourhood outside of Chicago where director Assia Boundaoui grew up, most of her neighbours think they have been under surveillance for over a decade. While investigating their experiences, Assia uncovers hundreds of pages of Operation Vulgar Betrayal, FBI documents that prove her hometown was the subject of one of the largest counter-terrorism investigations ever conducted in the United States before September 2001. No arrests or links to terrorist activity were ever made from the operation. The Feeling of Being Watched follows the examination of why a community fell under blanket government surveillance, the government secrecy shrouding what happened, and why her community feels like they’re still being watched today.
In the wake of September 11, 2001, Sibel Edmonds is approached by the FBI. As an American of Iranian and Turkish origin, Edmonds' linguistic skill-set makes her a valuable asset to the Language Services Unit, where she spends months translating high-security clearance documents. One day shortly after reporting the possible infiltration of her unit by Turkish spies to her supervisors and their supervisors, Edmonds' world is turned upside-down. Instead of seeing her colleague become the target of an investigation, she is interrogated, then unceremoniously fired and warned not to pursue her claims any further as she would be watched and listened to. Kill The Messenger documents both Edmonds' personal struggle to expose the criminality uncovered while at the FBI, and also the September 11 tied 'secret' itself--the network of nuclear black-market, narcotics and illegal arms trafficking activities.
The Newburgh Sting exposes the FBI's nationwide practice of targeting Muslim communities by luring unsuspecting impoverished citizens into traps to commit acts of terrorism, and then selling their arrests to the public as major law enforcement coups. As told by the defendants, lawyers, local Imams and a former career FBI agent, The Newburgh Sting depicts how four men living at the margins of society were entrapped by an FBI informant and lured into a wild plot involving bombing a wealthy Riverdale synagogue, and shooting stinger missiles to take down a military supply plane. Their arrest was misleadingly portrayed to the public as a counter-terror victory.
Informant
Informant follows the story of Brandon Darby--a radical-left activist turned FBI informant through a series of events starting with community support work in the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina in 2005, to the Republican National Convention in 2008. Brandon ends up turning fellow activists to the FBI for making Molotov cocktails in circumstances described by fellow activists as entrapment. So what happened? Did Brandon manipulate fellow activists into doing things they didn't want to do, or were some activists simply not engaging in a full analysis of the effectiveness of their strategies and tactics? In any event, was turning over activists to the FBI the right thing to do, even when nobody was hurt?
On April 19, 1995, Timothy McVeigh, a former soldier deeply influenced by the literature and ideas of the radical right, parked a truck with a five-ton fertiliser bomb in front of the Alfred P. Murrah Federal building in Oklahoma City. Moments later, 168 people were killed and 675 were injured in the blast. Oklahoma City traces the events that led McVeigh to that day from the perspective of the survivors, first-responders, investigators, and journalists who covered the events. The film provides an exploration of the convergence of various conservative religious movements and white supremacist militias that rose to prominence in the early 1990s, and were catalysed by the actions of government during that time.
A secret illegal project from the 1950s, 60s and 70s called COINTELPRO, represents the state's strategy to prevent resistance movements and communities from achieving their ends of racial justice, social equality and human rights. The program was mandated by the United States' FBI, formally inscribing a conspiracy to destroy social movements, as well as mount institutionalised attacks against allies of such movements and other key organisations. Some of the goals were to disrupt, divide, and destroy movements, as well as instilling paranoia, manipulation by surveillance, imprisonment, and even outright murder of key figures of movements and other people. Many of the government's crimes are still unknown. Through interviews with activists who experienced these abuses first-hand, COINTELPRO 101 opens the door to understanding this history, with the intended audience being the generations that did not experience the social justice movements of the 60s and 70s; where illegal surveillance, disruption, and outright murder committed by the government was rampant and rapacious. This film stands to provide an educational introduction to a period of intense repression, to draw many relevant and important lessons for the present and the future of social justice.
The Murder of Fred Hampton is a film which began with the intention of documenting Fred Hampton and the Illinois Black Panther Party during 1971, but during the film's production, Hampton was murdered by the Chicago Police Department and FBI. The film project then quickly split into two parts: the portrait and biography of Fred Hampton, and an investigative report into his murder. The result chronicles important historical context. Hampton was a radical activist and deputy chairman of the national Black Panther Party, during the civil rights and black power movements in the United States. Hampton was killed as part of COINTELPRO—the illegal "counter-intelligence program" run by the FBI, aimed at destroying domestic political organisations through surveillance, infiltration, disruption, threats, violence and assassinations.
1966, United States. A new revolutionary culture was emerging and it sought to overthrow the corrupt systems of power waging the invasion of Vietnam, amongst the struggle for equality and civil rights at home. Beginning with armed citizens' patrols to keep police accountable and challenge police brutality in Oakland California, The Black Panther Party put itself at the vanguard for social change, expanding in 1969 to community social programs, including free breakfast for school kids and community health clinics. This lead the FBI to call the movement "the greatest threat to the internal security of the country," and start an extensive government program called COINTELPRO to surveil, infiltrate, perjure, harass, discredit, destabilise and disintegrate the movement. This film chronicles the story arc of the Black Panthers successes and failures, through the voices of the people who were actually there: police, FBI informants, journalists, white supporters and detractors, and the Black Panthers themselves.
In March 1971, eight ordinary citizens broke into an FBI office in Pennsylvania, took hundreds of secret documents out, and mailed them to newspapers across the country to share them with the public. The group, calling themselves The Citizens' Commission to Investigate the FBI, undertook the actions at a time where suspicions about systemic abuse and manipulation of social and political movements by intelligence agencies were running high in the context of the Vietnam war and 1960s counter-culture. In doing so, these citizens uncovered the FBI's vast and illegal regimes, leading to insights about mass surveillance, intimidation, entrapment, and the use of provocateurs and informers for manipulation, and sabotage. Much of this would later go on to be known as part of a covert program called COINTELPRO that was run directly by J. Edgar Hoover to destroy social change movements—a history that is imperative to understand in the context of today, where state repression of social change movements continues.