Reaching into the Orwellian memory hole, War Made Easy exposes the some 50-year pattern of government deception and media spin that has dragged the United States into one war after another from Vietnam to Iraq. Using archival footage of official distortion and exaggeration from LBJ to George Bush, this film reveals how the American news media have uncritically disseminated the pro-war messages of successive governments -- paying special attention to the parallels between the Vietnam war and the war in Iraq...
Crazy Rulers of the World is a series that investigates what happens when chiefs of the United States intelligence agencies and the army began believing in very strange things. With first-hand access to the leading characters in the story, filmmaker Jon Ronson examines the extraordinary and bizarre national secrets at the core of the war on terror.
This film comprehensively documents the use of chemical weapons--particularly the use of incendiary bombs--along with hordes of other horrific indiscriminate violence against civilians and children by the United States military in the city of Fallujah during the invasion of Iraq in November 2004. The cases portrayed involve the use of white phosphorus and other substances similar to napalm, such as Mark-77, which constitute clearly defined war crimes involving chemical weapons. Interviews with ex-military personnel involved in the Fallujah offensive back up the case for the use of such weapons by the United States, while reporters stationed in Iraq discuss the government's attempts to suppress the news by covert means.
Mirage Men examines evidence of a conspiracy by the United States military to fabricate UFO folklore over decades in order to deflect attention away from classified military projects. The film profiles a retired Special Agent, Richard Doty, who worked for the United States Department of the Air Force Office of Special Investigations, and the United States Air Force Office of Special Investigation, and speaks about his role in special operations that targeted both individual people, and the public at large for many years. The film also weaves in the viewpoints of others, either in the sphere of the myths, or working to uncover their origins.
After Iraq invaded Kuwait in 1990, the United Nations (backed strongly by the US and UK) imposed harsh sanctions on Iraq that lasted for 10 years (1991-2001); the harsh restrictions on imports of everything, including access to key medicines, resulted in over a million deaths, more than half a million of which were women and children. That's more deaths than the two atomic bombs dropped on Japan and the events of September 11 combined. The purpose was regime change, but it never came. The overwhelming majority of those killed were the poor, elderly, women and children. Empirically, sanctions overwhelmingly punish the poor, the destitute. While the sanctions were in place, the richest people in control of the resources (Saddam Hussein et al.) still had everything they wanted: food, cars, mansions, free access to medicines, etc...
Robot Wars
Robot Wars visits companies in the United States that are producing robots for the military to disarm bombs, fly unmanned aircraft (drones), withstand repeated attacks and even choose targets and fire without any human intervention. The rapid development of autonomous robots and the use of them right now is surging ahead at a crazy rate, all with little regard to ethical and psychological questions, concerns about technological privilege and other obvious impacts. With military robots currently being operated using video game controllers, is the line being blurred between fantasy and reality?
Produced while the invasion was in full swing, Iraq for Sale investigates some the many private contractors and consultants that were brought into to Iraq as part of the United States military machine. Four major contractors are profiled: Blackwater, K.B.R.-Halliburton, CACI and Titan, along with investigations of human rights violations, systemic misconduct, corruption, and profiteering. The film posits what damage is done to the 'average citizen' when corporations decide to wage war. For those in opposition to war and corporate power, the connection between the invasion of Iraq and the private corporations who profit from the fighting is plain to see. For those who still may not be so easily convinced, the film not only explores the questionable motivations of the corporate decision-makers whose wartime profiteering has affected the lives of countless soldiers and their families, not mention the lives of millions of civilians, but also the increasingly negative international reputation of the United States as a result.
By comparing the confluence of ideas about modifying behaviour using shock therapy and other forms of sensory deprivation (which culminated in the top-secret CIA project called MKULTRA during the 1950s) alongside the metaphor of similar shock treatment modifying national economics using the teachings of Milton Friedman and the Chicago School of economics, The Shock Doctrine presents the workings of global capitalism in this framework of how the United States, along with other western countries, has exploited natural and human-engineered disasters across the globe to push through reforms and set-up other mechanisms that suit those in power and 'shock' other countries into a certain wanted behaviour. Chronologically, some historical examples are the using of Pinochet's Chile, Argentina and its junta, Yeltsin's Russia, and the invasion of Iraq. A trumped-up villain always provides distraction or rationalisation for the intervention of the United States—for example, the threat of Marxism, the Falklands, nuclear weapons, or terrorists—and further, is used by those in power as more justification for the great shift of money and power from the many into the hands of the few(er).
Using interviews and frontline footage, Vietnam -- The Quiet Mutiny reveals the internal sense of disillusionment and frustration born from the rift between bureaucracy and soldiers, that triggers the withdrawal of the United States military from Vietnam. As the US employs psychological warfare against the Vietnamese, reporter John Pilger finds himself unable to obtain meaningful information from the military—a press conference he attends is nicknamed "the 5 o'clock follies" for the evasive nature of the proceedings. And so it is with the grunts, the "wheels of the green machine," that Pilger finds a very human side to the US presence in Vietnam: soldiers who were once ready to serve their country, now doubtful of their purpose there. Plied with visits from Miss America and ignored by Vice President Spiro Agnew, they experience the war in a way many of their superiors do not.
How does the military train the solider of tomorrow? Video games. The most popular games are those that replicate as close as possible the war events as seen on the news. Such games now far outpace the biggest Hollywood blockbuster movies, popular music, and best-selling books, combined. What does this complete immersion in high-tech war mean for our political culture? As well as those directly affected by state violence? What does it mean when the technological sophistication of modern militarism become forms of mass entertainment? Returning Fire profiles three artists and activists that decided these questions needed to be answered. We see how Anne-Marie Schleiner, Wafaa Bilal, and Joseph Delappe moved dissent from the streets to the screens, infiltrating war games in an attempt to break their hypnotic spell. The results ask all of us--gamers and non-gamers alike--to think critically about what it means when drones and remote warfare become computer games and visa versa. Can we reflect on our capacity to empathise with people directly affected by the trauma of real war?
They brought us war in Iraq, the promotion of "American global leadership," pre-emptive strikes; the "spreading of Democracy." This is the Project for the New American Century. But what do the hawks in Washington have in store for the world now? The War Party investigates this group of beurocrats responsible for the Project for the New American Century, called the neo-conservatives. This interconnected, dispersed group are running the White House in concert of the Bush years and family dynasty. Is it surprising how little has changed?
Kanehsatake: 270 Years of Resistance documents the 'Oka Crisis' of 1990 in which the government of Oka, Canada, pushed for plans to develop a private golf course and new luxury housing on sacred indigenous land. The film captures the events as they unfold, from the beginnings as frivolous government 'negotiations' to the resulting siege by the Canadian Army and local police...
In 2004, during the invasion of Iraq, the public learned of systemic sexual abuse, torture, rape and even murder going on inside Abu Ghraib prison in Baghdad. Photographs taken by the soldiers themselves were at the centre of the scandal, and seared public consciousness. Standard Operating Procedure sets out to examine the context of these photographs. Why were they taken? What was happening outside the frame? The Abu Ghraib photographs serve as both an expose and a coverup. An expose, because the photographs offer us a glimpse of the horror of Abu Ghraib; and a coverup because they convinced journalists and readers they had seen everything, that there was no need to look further...
John Pilger and David Munro look behind political rhetoric to discover the hidden world of international arms dealing...
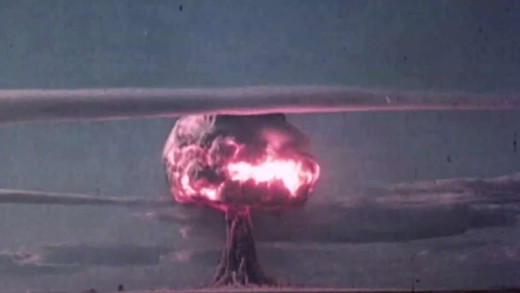
Atomic Confessions investigates the devastating effects of atomic weapons testing carried out in Australia by the British military during the 1950s. Members of the Australian Army, Air Force and Navy detail former top-secret aspects of the tests, while prominent Aboriginal Elders describe the real impacts on the ground. Using archival film and photographs, as well as eye witness accounts, Atomic Confessions chronicles the consequences of nuclear testing imposed on the Australian people, and the land, showing that these tests are not just skeletons of the past...
The Road to Guantánamo is a docu-drama about the incarceration of three British citizens--otherwise known as the Tipton Three--who were captured in Afghanistan in 2001 and detained for more than two years by the United States in Guantánamo Bay Naval Base, Cuba. The three were held in mostly solitary confinement and without legal representation for that time, after being released in 2004 without charge. Based on interviews, The Road to Guantánamo reenacts their experience in the camp, depicting the use of torture techniques such as stress positions, and attempts by the United States Army and CIA interrogators to extract forced confessions of involvement with al-Qaeda and the Taliban.
By charting the history of the anti-war movement against the political backdrop of the atomic age, Beating The Bomb examines the current state of 'nuclear deterrence' brought about by the nuclear age stemming from the end of World War II, when the United States nuked Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Specifically, the anti-nuclear movement and the founding of the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament in 1958 amongst others, fight for and end to the British Nuclear Weapons program, which from its inception, was closely tied to The Manhattan Project and still is to this day...
Cover Up -- Behind The Iran-Contra Affair is a thorough investigation into information suppressed during the Iran-Contra hearings in 1987 where it was found that senior officials in the United States government secretly facilitated the sale of arms to Iran. The film reveals a shadow government of former CIA operatives, drug smugglers, top US military personnel and others, revealing evidence of the history of CIA involvement in drug running from the Vietnam heroin era to the Central American cocaine epidemic -- raising serious questions about the so-called "war on drugs" and other government movements since the 1980s...
The Kill Team
The Kill Team profiles four young American men, who referred to themselves as the "Kill Team," that carried out a string of war crimes in 2010, during the United States' invasion of Afghanistan, systematically murdering Afghan citizens. The film focuses on Private Adam Winfield who attempted, with the help of his father, to alert the military to the murders his platoon was committing. His pleas went unheeded. Faced with threats to his life from superior officers and other members of the military, Winfield makes a split-second decision that changes his life forever. The Kill Team follows Winfield and his family through the wartime events and legal proceedings that follow, interspersed with interviews of the other soldiers involved, and video footage from Afghanistan, revealing first-hand revelations of a war culture rooted in hatred, social pressure, and sociopathy.
The untold history of The Project for the New American Century is no more. This film exposes how every major war in US history was based on a complete fraud with video of insiders themselves admitting it. This documentary shows how the first film theatres in the US were used over a hundred years ago to broadcast propaganda to rile the American people into the Spanish-American War; the white papers of the oil company Unocal which called for the creation of a pipeline through Afghanistan and how their exact needs were fulfilled through the US invasion of Afghanistan; how Halliburton under their "cost plus" exclusive contract with the US Government went on a mad dash spending spree akin to something out of the movie Brewster's Millions...
Between 1964 and 1973 the United States conducted a secret war in Laos -- dropping over 2 million tons of bombs, making it the most heavily bombed country in history. Millions of 'cluster bombs' did not explode when dropped, leaving the country massively contaminated with "bombies" which are as dangerous now from when they fell over 30 years ago. Bombies documents unexploded cluster bombs through the personal experiences of a group of Laotians and foreigners who go about dismantling the bombs. These weapons are still a standard part of the United States military arsenal and were recently dropped in Kosovo, Afghanistan and Iraq...
Ghosts of Abu Ghraib examines the sexual abuse, torture, rape, and murder of detainees at Abu Ghraib prison at the hands of US military police in the fall of 2003. The film shows how the abuse was systemic of the military-intelligence complex, flawing the "bad apples" theory that was sprouted through the media at the time. By making reference to Stanley Milgrim's obedience experiments of the 1960s, the film asks: How can ordinary people take these actions? And what orders came from the chain of command?
John Pilger returns to the Occupied Territories of the West Bank and Gaza where, in 1974, he filmed a documentary with the same title -- Palestine Is Still The Issue -- a film about the same issues, a nation of people, the Palestinians, forced off their land and subjected to military occupation by Israel. Pilger hears extraordinary stories from Palestinians, though most of his interviews are with Israelis whose voices are seldom heard, including the remarkable witness of a man who lost his daughter in a suicide bombing. But for Palestinians, the overriding, routine terror, day after day, has been the ruthless control of almost every aspect of their lives, as if they live in an open prison. This film is about the Palestinians and a group of courageous Israelis united in the fight to be free...
Agent Orange was the codename for one of the herbicides and defoliants used by the United States military as part of its chemical warfare program--Operation Ranch Hand--which ran for ten years during the Vietnam War from 1961 to 1971. During this time, the military sprayed nearly 80,000,000 litres of toxic chemical and defoliants mixed with jet fuel in Vietnam, eastern Laos and parts of Cambodia. The supposed goal being to destroy forested and rural land, depriving guerrillas of cover and to induce forced-draft-urbanisation, destroying the ability of peasants to support themselves, forcing them to flee to the cities dominated by US forces, depriving the guerrillas of their rural support base and food supply...
The Secret Government, as its title suggests, is essentially an investigation into the processes, plans, operations and persons responsible for systemic abuses of power at senior levels of the United States government during the 1980s. The film covers multiple covert operations and secret projects, but takes a particular focus on the Iran–Contra affair of 1986, where Ronald Regan secretly facilitated the illegal sale of arms to Iran—which was the subject of an arms embargo at the time—to support a right-wing terrorist group called "The Contras," and also make obscene profits from the sale of such weapons. Transported to the political happenings of today, The Secret Government is a call to remember history, and see that mass profits from weapons dealing running covert/secret wars were a reality then, and now, as well as to reveal just how far institutionalised propaganda and obfuscation works to conceal these home truths, still generations later.
By risking torture and life in jail, courageous young citizens of Burma live the essence of journalism as they document the uprisings against the military regime in 2007. Armed with small handycams, the Burma VJs stop at nothing to make their reports from the streets of Rangoon. Their video footage is smuggled out of the country and broadcast back in via satellite and offered up for use in the international media. The whole world witnesses single event clips made by the VJs, but for the very first time, the individual images have been put together here to tell a much bigger story...
The Panama Deception documents the invasion of Panama in December 1989—codenamed Operation 'Just Cause.' The film gives context to the events which led to the invasion, and explores the real impact on the ground and devastating aftermath—all contrary to the views portrayed by mainstream media and rhetoric espoused at the time by government officials in the Bush administration. News footage and media critics reveal the extent of media control and self censorship of the invasion, relevant to any news coverage today, particularly during times of war.
As the United States developed the world's first nuclear weapons in secret, it was surprised at the speed in which the USSR was able to also develop such weapons, and that such developments would lead to an unprecedented arms race. The USSR was able to obtain all the nuclear discoveries made by scientists who worked on the top-secret Manhattan Project through a very unusual spy, Elizabeth Zaroubin. She managed to gain the trust of great researchers, such as Einstein, in a story comparable to some of the best spy novels ever written.