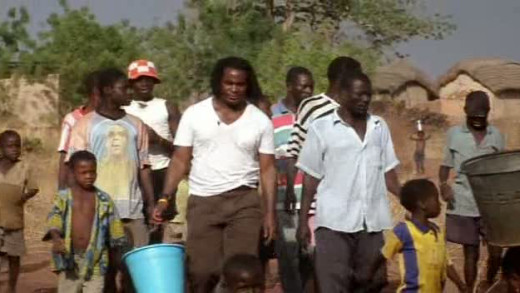Filmed in Thailand and the Philippines in July 2007, Squeezed tells the story of how free trade agreements and globalisation are changing the lives of millions of people living in the Asia-Pacific region with APEC. Featuring interviews with farmers, workers and slum-dwellers, the film travels across the landscapes of Asia, from the lush rice paddies of Thailand to squatter settlements perched on a rubbish dump in urban Manila. Documenting these contrasts and contradictions, Squeezed accounts the impact of globalisation...
Can't Get You Out of My Head: An Emotional History of the Modern World is a six-part series that explores how modern society has arrived to the strange place it is today. The series traverses themes of love, power, money, corruption, the ghosts of empire, the history of China, opium and opioids, the strange roots of modern conspiracy theories, and the history of Artificial Intelligence and surveillance. The series deals with the rise of individualism and populism throughout history, and the failures of a wide range of resistance movements throughout time and various countries, pointing to how revolution has been subsumed in various ways by spectacle and culture, because of the way power has been forgotten or given away.
The 2008 'financial crisis' was a systemic fraud in which wealthy finance capitalists stole trillions of public dollars all over the world. No one was jailed for this massive crime, the largest theft of public money in history. Instead, the rich forced working people across the globe to pay for their 'crisis' through punitive austerity programs that gutted public services and repealed workers' rights. Capitalism Is The Crisis shows and explains this fundamental functioning of the global economy, while visiting protests from around the world against it, revealing revolutionary paths for the future. Special attention is devoted to the current situation in Greece, the 2010 G20 Summit protest in Toronto Canada, and the remarkable surge of solidarity in Madison, Wisconsin.
The discrepancies between the "War on Terror" and the facts on the ground in Afghanistan and Iraq are many. In 2001, as the bombs began to drop, George W. Bush promised Afghanistan, "the generosity of America and its allies." Now, the familiar old warlords are retaining their power, religious fundamentalism is expanding its grip and military 'skirmishes' continue routinely. In "liberated" Afghanistan, America has its military base and pipeline access, while the people have the warlords who are, as one woman says in the film, "in many ways worse than the Taliban."
Why did appointed officials of the Australian Reserve Bank and its employees break sanctions in Iraq and cosy up to Saddam Hussein through a frontman during the late 1990s, early 2000s and beyond? Why did a former Deputy Governor and other directors hand-picked by the Reserve Bank to safeguard its subsidiary companies from corruption, end up--over a decade--overseeing some of the most corrupt business practices possible? How did they allow millions of dollars to be wired to third parties in foreign countries--including a known arms dealer--in order to win banknote contracts knowingly using bribery and supporting corruption?
Robert Beckford visits Ghana to investigate the hidden costs of rice, chocolate and gold and why, 50 years after independence, a country so rich in 'natural resources' is one of the poorest in the world. He discovers child labourers farming cocoa instead of attending school and asks if the activities of multinationals, the World Bank and International Monetary Fund have actually made the country’s problems worse...
The Big Sellout reveals the reality of privatisation and globalisation by examining the corporate takeover of basic public services throughout the world, such as water supply, electricity, public transportation, and public health care. In South America, Asia, Africa, but also in Europe and the United States, filmmaker Florian Opitz talks to the architects of the new economic world order, as well as to ordinary people who have to deal with the real direct effects. The result is a tapestry of narratives the world over that show where the dogma of privatisation cames from, who profits from it, what societies lose, and why resistance is so important.
The End of Poverty? traces the growth of global poverty back to colonisation in the 15th century to reveal why it's not an accident or simple bad luck that there is a growing underclass around the world. Featuring interviews with a number of economists, sociologists, and historians, the film details how poverty is the clear consequence of free-market economic policy which has allowed powerful nations to exploit poorer ones for their assets, turning the money back to the hands of the concentrated few. This also follows on to how wealthy nations--especially the United States--thereby exert massive debts, seize a much disproportionate exploit of the natural world, and how this deep imbalance has dire consequences on the environment and on people...
Did you know that the legal system recognises a corporation as a person? What kind of 'person' is it then? What would happen if it sat down with a psychologist to discuss its behaviour and attitude towards society and the environment? Explored through specific examples, this film shows how and why the modern-day corporation has rapaciously pressed itself into the dominant institution of our time, posing big questions about what must be done if we want a equitable and sustainable world. What must we do when corporations are psychopaths?
For millions of people, the global economic collapse has generated curiosity about how money systems actually work, as opposed to how they're portrayed, especially when so many financial pundits seem to be baffled. In The Ascent of Money, economist Niall Ferguson works through some history that created today's money system, visiting the locations where key events took place and poring over actual ledgers and documents, such as the first publicly traded share of a company. Viewed with a critical eye, this series aims to show how the history of money is indeed at the core of civilisation, with economic strength determining political dominance, wars fought to create wealth and individual financial barons determining the fates of millions.
War By Other Means examines the policy of western banks making loans to so-called 'third world' countries, which are then unable to meet the crippling interest charges—debt used as a weapon. The film primarily analyses 'Structural Adjustment Programs,' which are proclaimed to enable countries to compete in the 'global economy,' but have the opposite effect of lowering wages which in turn further transfers the wealth from the poor to the rich.
The Spider's Web: Britain's Second Empire shows how Britain transformed from a colonial power into a global financial power. At the demise of empire, the City of London's financial interests created a web of offshore secrecy jurisdictions that captured wealth from across the globe and hid it behind obscure financial structures, and webs of offshore islands. Today, up to half of global offshore wealth may be hidden in British offshore jurisdictions, and these are now the largest players in the world of international finance. Based in part on the book Treasure Islands by expert Nicholas Shaxson, and through contributions from former-insiders, academics, and campaigners for justice, The Spider's Web reveals how, in the world of international finance, corruption and secrecy have prevailed over regulation and transparency, and how the United Kingdom is a pioneer of the modern corrupt global economy.
Exploring the collusion between the richest people in the United States and the figureheads of political power in government, this film focuses on Park Avenue in New York which is currently the home to the highest concentration of billionaires in the United States. Across the river in Manhattan, less than five miles away, Park Avenue runs through the South Bronx which is home to the countries' poorest. The disparity of wealth has never been so stark and has accelerated extraordinarily over the last 40 years. As of 2010, 400 people controlled more wealth than the bottom 50 percent of the population—150 million people—as well as seizing political power. Park Avenue travels through this to illustrate why the concept of so-called "upward mobility" is a myth perpetuated by the rich, and also to unpack the workings of plutocracy and capitalism—the current-day rule by the rich, and the implications of this collusion of power and control.
Money is a new form of slavery and is only distinguishable from the old slavery simply by the fact that it is impersonal--that there is no human relation between master and slave. Debt in government, corporate and household has reached astronomical proportions. Where does all this money come from? How could there be that much money to lend? The answer is that there isn’t...
The Wall Street Code explores the once-secret lucrative world of prolific algorithmic trading by profiling an inside programmer who, in 2012, dared to stand up against Wall Street and its extreme culture of secrecy, to blow the whistle on insights into the way the modern global money market works. His name is Haim Bodek—aka 'The Algo Arms Dealer'—and having worked for Goldman Sachs, his revelations speak to the new kind of wealth made only possible by vast mathematical formulas, computer technologies and clever circumventions of laws and loophole exploits. Vast server farms and algorithms working beyond the timescale of human comprehension, have largely taken over human trading on the global financial markets for decades. What are the implications of that? The algorithms seem to have a life of their own. Snippets of code secretly lie waiting for the moment that your pension fund gets on the market; trades done in nanoseconds on tiny fluctuations in stock prices. And the only ones who understand this system are its architects—the algorithm developers. The Wall Street Code provides just a small insight into this new world of high-frequency trading, amongst other things...
By comparing the confluence of ideas about modifying behaviour using shock therapy and other forms of sensory deprivation (which culminated in the top-secret CIA project called MKULTRA during the 1950s) alongside the metaphor of similar shock treatment modifying national economics using the teachings of Milton Friedman and the Chicago School of economics, The Shock Doctrine presents the workings of global capitalism in this framework of how the United States, along with other western countries, has exploited natural and human-engineered disasters across the globe to push through reforms and set-up other mechanisms that suit those in power and 'shock' other countries into a certain wanted behaviour. Chronologically, some historical examples are the using of Pinochet's Chile, Argentina and its junta, Yeltsin's Russia, and the invasion of Iraq. A trumped-up villain always provides distraction or rationalisation for the intervention of the United States—for example, the threat of Marxism, the Falklands, nuclear weapons, or terrorists—and further, is used by those in power as more justification for the great shift of money and power from the many into the hands of the few(er).
2009, pornography has grown into a $10 billion business, and some of the world's most-known corporations are silently sharing in the profits. Companies like Time Warner, Marriott, and Vodaphone earn huge amounts of revenue by piping pornography into homes and hotel rooms, but you won't see anything about it in their company reports. Even the Catholic Church invests in companies that distribute pornography, along with pension funds that earn huge profits from investing in ventures that relate to porn. Hardcore Profits is a two part television series that explores how in the 21st century, pornography has never been more profitable, nor more pervasive.
There are plenty of anarchists in the world. Many have committed robbery or smuggling for their cause. Fewer have discussed strategies with Che Guevara or saved the skin of Eldridge Cleaver, the leader of the Black Panthers. There is only one who has done all that, and also brought to its knees the most powerful bank in the world by forging travellers cheques, without missing a single day of work bricklaying. He is Lucio Urtubia from a tiny village in Navarra in North of Spain. Lucio, 75, now lives in Paris, still doing valued political work. Lucio has been protagonist and witness to many of the historic events of the second half of the 20th century. His family was persecuted by Franco's regime; he was on the streets of Paris for the phenomenon of May of 1968; he actively supported Castro's revolution; and helped thousands of exiled people by providing false documents to them. But without a doubt, his greatest triumph came in the second half of the 1970s where he swindled 25 million dollars from the First National Bank--or Citibank--to later invest the money in causes he believed in.
The myths of globalisation have been incorporated into much of our everyday language. "Thinking globally" and "the global economy" are part of a jargon that assumes we are all part of one big global village, where national borders and national identities no longer matter. But what is globalisation? And where is this global village? In some respects you are already living in it. The clothes in your local store were probably stitched together in the factories of Asia. Much of the food in your local supermarket will have been grown in Africa...
In Requiem for the American Dream, renowned intellectual figure Noam Chomsky deliberates on the defining characteristics of our time—the colossal concentration of wealth and power in the hands of the few and fewer, with the rise of a rapacious individualism and complete collapse of class consciousness. Chomsky does this by discussing some of the key principles that have brought this culture to the pinnacle of historically unprecedented inequality by tracing a half century of policies designed to favour the most wealthy at the expense of the majority, while also looking back on his own life of activism and political participation. The film serves to provide insights into how we got here, and culminates as a reminder that these problems are not inevitable. Once we remember those who came before and those who will come after, we see that we can, and should, fight back.
Inside Job provides a comprehensive analysis of the global financial crisis of 2008, which at a cost over $20 trillion, caused millions of people to lose their jobs and homes in the worst recession since the Great Depression, and nearly resulted in a global financial collapse. Through interviews with key financial insiders, politicians, journalists, and academics, Inside Job traces the rise of a rogue industry which has corrupted government and academia...
The Power of the Fed investigates how the United States central bank's actions have played out over the years on Wall Street versus Main Street, since the last financial crash of 2008. The film traces how the experiment the Fed began in 2008 has been dramatically ratcheting up, peaking with the COVID-19 crisis in 2020. But, of course, rather than help correct from the huge corruption and financial abstractions that caused the 2008 crash, the fed has doubled down on its policies of "quantitative easing" which have gone on to help widen the greatest inequality of wealth in history, pushing financial products even further removed from the economy, driving inflation, automation, and worsening the impending cycles of boom and bust. The rise of speculative cryptocurrencies and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) has only fueled the mania, as economic volatility increases.
Over six desperate days in October 1929, the New York Stock Exchange crashed leading to the collapse of three thousand banks, taking people's savings with them. In a matter of days, the United States economy was obliterated. The crash was followed by a devastating worldwide depression that lasted until the Second World War. Finances did not regain their pre-crash values until 1954. This film recounts the story of a financial disaster that we hoped could never happen again, revealing the familiar tune of cheap credit, consumerism, greed, corruption and cronyism in the current-day financial crisis...
Recorded by over 100 media activists, this film tells the story of the enormous street protests in Seattle, Washington in November 1999, against the World Trade Organisation summit. Vowing to oppose--among other faults--the WTO's power to arbitrarily overrule nations' environmental, social and labour policies in favour of unbridled corporate greed, thousands of people from all around the United States came out in force to stop the summit. Against them was a brutal police force and a hostile media. This Is What Democracy Looks Like documents the struggle, as well as providing a narrative to the history of success and failure of modern political resistance movements.
Based on the book of the same title by Juliet Schor, The Overspent American scrutinises the form of consumerism ever-pervasive in this current era that is driven by upscale spending and debt; shaped and reinforced by a media system driven by commercial interests. We're encouraged from all angles to spend money we don't have, working longer hours than ever before. Illustrated with hundreds of examples, The Overspent American draws attention to both the financial and social costs of this giant consumption machine, where the frivolous and relentless search for "happiness" and identity is espoused by advertising.
25 Million Pounds details the collapse of Barings Bank in the mid 1990s primarily by a broker called Nick Leeson, who lost £827 million ($1.3 billion) by speculating on futures contracts. The film contextualises the downfall as the history of Barings Bank was one of the oldest and most prestigious merchant banks in Britain, run by the same family for decades with extensive ties to Britain's elites. But in the late 19th century Barings almost went bankrupt after investing heavily in South American bonds, including backing the construction of a sewer system in Buenos Aires. The bank was saved by The Bank of England, but Edward Baring, the head of the bank, was financially ruined and never recovered. This film explores the culture of Barings and of the financial markets during the 1990s, and how Nick Leeson was able to cause another huge loss of money to the bank, this time bankrupting the company. He did this by claiming fictitious profits on the Singapore International Monetary Exchange and using money requested from London as margin payments on fictitious trades to finance his loss-making positions. It's also the profile of a stereotypical corporate psychopath, as Leeson himself explains how he was able to manipulate those around him to achieve his ends and rationalise his actions.
Housing is fundamental human right. But in cities all around the world, housing affordability is decreasing at record pace. The local working and middle classes have become unable to afford housing in major cities: London, New York, Berlin, Hong Kong, Toronto, Tokyo, Valparaiso, Sydney, Melbourne, Caracas, Barcelona, Paris, Amsterdam, Stockholm... the list seems endless. People are being pushed out of their very own homes--because living in them has rapidly become unaffordable. Told through the eyes of Leilani Farha, a United Nations special rapporteur on housing, Push touches on the foundations of the crisis, as we follow the rise of abstract finance and the pervasive influence of neoliberalism that conjures a perfect storm: the global financial crisis of 2008--where houses packaged as "complex financial instruments" were the core of the crisis. Then, once the financial industry was bailed out by the public to the tune of trillions of dollars, financiers bought up millions of houses around the globe for cents on the dollar, and their power and influence has only increased in the subsequent decades. Farha travels all around the world, speaking to people that now spend 90% of their income on rent, after wages have stayed stagnant since 1970s, and how large corporations swallow up entire communities, guided by the same politik. She says we still need to confront those old ideas--the financialisation of the housing 'market.' "There's a huge difference between housing as a commodity and gold as a commodity." These systems don't consider the people they extract from.
Obey is a video essay based on the book "Death of the Liberal Class" by author and journalist Chris Hedges. The film charts the rise of corporatocracy and examines the trending possible futures of obedience in a world of unfettered capitalism, globalisation, staggering inequality and environmental crisis -- posing the question, do we resist or obey?