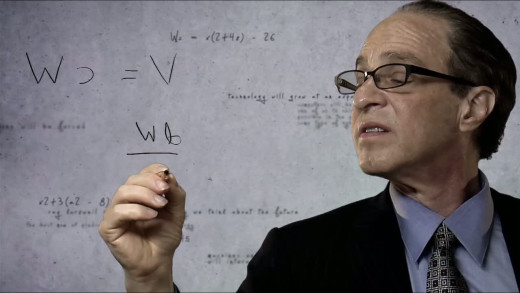The Truth About Killer Robots considers several cases where humans have been killed from interactions with automatic machines. From the Volkswagen factory in Germany, to workers in Chinese sweatshops assembling smartphones, to a bomb-carrying police droid in the United States, the film exposes this culture's fundamental fascination with machines, while illustrating the insatiable expansion of capitalism via automation and machine redundancy. Also explored are 'self-driving' cars; surveillance devices; humanless-stores, automated pizzas, robotic supermarkets and hotels; so-called 'sex' robots; and vast data gathering machines such as Facebook, which have subverted notions of real human interaction and intimacy. Told through the machine lens of engineers themselves, journalists and philosophers, the film attempts to go beyond the deaths of humans to reveal some of the ways that robots affect this culture in general. Not just by the displacement of labour, but fundamentally as humans of this culture adjust their lives to the rhythms of more and more machines, basic human faculties atrophy, and true connection to the real world and each other becomes more remote and strenuous, at precisely the same time where we need each other the most.
Technocalyps
The latest findings in genetics, robotics, artificial intelligence, bionics and nanotechnology appear in the media frequently, but almost no analysis is found of their common aim which is to "exceed human 'limitations' and capability"—literally to 'transcend' humanity: transhumanism. This three part series covers the notion of transhumanism, the desire of technologists to become physical machines in totality, prompting serious physical, ethical, philosophical and practical questions. Will the transhumanists achieve their sacred so-called singularity? And what will that mean in the real world?
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, is spouted as the ability of machines to "think" [sic] at a speed and depth far beyond the capacity of any human. Proponents of these digital technologies claim their systems are used in ways that are beneficial for society. But as we see, the current use of AI isn't necessarily aligned with the goals of building a better society. There still remain escalating concerns about labour, the future of work, privacy, the surveillance society, and social control--all valid criticisms that go back many decades--while the rivalry for technological supremacy between the United States and China mirrors the dynamics of the cold war. In the Age of AI is an investigation that touches on these areas, providing a platform to ask fundamental questions about unrestrained technological escalation.
The Intelligence Revolution is an extolling and largely non-critical account by advocate Michio Kaku who unflinchingly explains how artificial intelligence will "revolutionise homes, workplaces and lifestyles," and how virtual worlds will apparently become "so realistic" that they will "rival" the real physical world. Robots with "human-level intelligence" may finally become a reality according to Kaku, and in the ultimate stage of scientific mastery, the era of control imperative and domination, this culture will seek to merge human minds with so-called machine intelligence. Also, for the first time, we see how a severely depressed person can be turned into a happy person at the push of a button—all thanks to the convergence of neuroscience and microtechnology. What's wrong with such developments? And the larger culture such that technologies like this are being developed in the first place? How do such prospects impact the real physical world and the real physical lives of all of us?
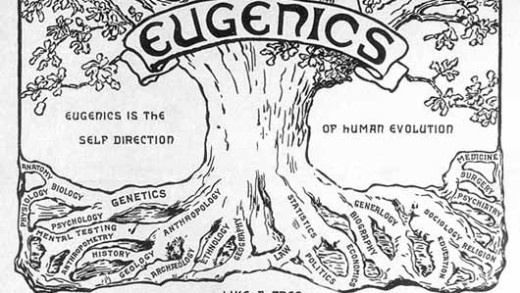
Transhumanists claim a beautiful and apparently now-not-so-distant utopian future made possible by artificial intelligence, life extension and cybernetic technologies. But upon examining the convergence of these technologies and the history behind them, Age Of Transitions details how this movement of "transcending human limits" was born out of pseudo-science eugenics, and what the implications are for a world divided by the have's and have-not's.
Ray Kurzweil, noted inventor and futurist, is a man who refuses to accept physical reality and the inevitability of death. Instead, he claims that the trending exponential increase in the growth of information technology can continue indefinitely, and that a so-called "singularity" will emerage—a point where humans and machines will converge, allowing one to "transcend" biological "limitations." But there are many who share deep concerns about the consequences of working towards Kurzweil's world...
The latest in the string of controversies as part of the United States' ongoing "war on terror", is the military's growing reliance on "Unmanned Aerial Vehicles" otherwise known as 'drones', evidenced by the international reaction to recent drone missile attacks along the border in Pakistan. The military is also deploying other technological advancements alongside, such as robots in the battlefield and drones that work in swarms. Is this just a big computer game? A new tech-driven arms race? It doesn't end there though -- drones are now creeping into use by police and the intelligence services as a surveillance tool, and even into commercial and civilian use...
Robot Wars
Robot Wars visits companies in the United States that are producing robots for the military to disarm bombs, fly unmanned aircraft (drones), withstand repeated attacks and even choose targets and fire without any human intervention. The rapid development of autonomous robots and the use of them right now is surging ahead at a crazy rate, all with little regard to ethical and psychological questions, concerns about technological privilege and other obvious impacts. With military robots currently being operated using video game controllers, is the line being blurred between fantasy and reality?
Just as mobile phones and wireless capability dramatically changed the way technology interacts with modern society, drones--or 'Unmanned Aerial Vehicles'--are set to become the next major influence in technocratic life, directly impacting and seriously expanding the already extensive capabilities of surveillance. Rise Of The Machines takes a look at already developed drone technology and how governments, military and even civilians are rushing to adopt the gadgets which can be purchased off the shelf for just a few hundred dollars and controlled by already existing smart phones. So what will a world of drones look like? And what of the many, serious, unexplored implications on how society will function in a world of drones?
Over the past decade, the United States military has shifted the way it fights its wars, deploying more technological systems in the battlefield than human forces. Today there are more than 7,000 drones and 12,000 ground robots in use by all branches of the military. These systems mean less deaths for US troops, but increased killings and precision elsewhere for the United States war machine. With lethal drone strikes being carried out in secret by the CIA and occurring outside of officially declared war zones such as Pakistan, Yemen and Somalia, the secret use of robots and drones in this way evokes serious questions about the operations of the United States and what this means for the rest of the world as more and more autonomy is developed for these technologies.
My Sex Robot
Meet Roxxxy, the world's first "sex" robot, and the strange men who've been yearning for "her" as an obedient android "sex partner." Roxxxy's inventor, Doug, is working on finely tuning the robot to be the perfect android sexual "companion" and has a queue of men eagerly awaiting a one night stand with it to test the technology of their fantasies. But how did this come about? My Sex Robot follows the lives of three men in attempt to find out. Delosian remembers from the age of 13 watching Bionic Woman and Six Million Dollar Man and it blew his mind. What he saw triggered his view of an ideal woman. Kaiso speaks of a similar experience sexualising mannequins from department stores. But for Edward, robot sex as already arrived. He has found it by converting his real-life girlfriend into a robot simulation. All these men speak about the power, control, predictability, and obedience that sex robots bring, as opposed to relationships with real human beings. As a result, My Sex Robot presents a startling reality of emerging technologies with already-existing myriad sociological and psychological implications.
Drone
In the wake of the September 11th attacks, amongst the ravaging of war, the United States has been secretly deploying drones to carry out assassinations throughout the Middle East. The drones are increasingly piloted by the likes of young computer gamers groomed by screen culture and computer games of war, where in many cases, the Pentagon is directly involved in the creation of such games as recruitment tools, actively working to lure young people proficient with technology into the new era of the military-industrial-complex. Drone unravels this complex phenomenon while travelling to places such as Waziristan, where innocent civilians, including children and rescue workers are routinely secretly killed, where families and communities ravaged by the drone strikes search for understanding, accountability and adjustment to the daily horrors. The film also takes a look at the young people sitting behind the screens of the new war machines, half a world away, that actually pull the trigger, asking what kind of world is being built in the rise of seemingly endless and lucrative war driven by technological escalation.
Kevin Warwick is a renowned researcher in the precarious field of cybernetics, the study of 'artificial intelligence,' human-control functions, robotics and so-called "cybernetic organisms." His work, as self presented here, shows how implant and electrode technology can be used to control human brain functions, to create biological brains for robots, to enable so-called "human enhancement" and treatment for neurological illnesses. The end goal is transcending human "limitations" or transhumanism, according to Warwick, which inevitably stirs up many social, ethical and practical questions. What are the implications of this work, and this world view?