Agent Orange was the codename for one of the herbicides and defoliants used by the United States military as part of its chemical warfare program--Operation Ranch Hand--which ran for ten years during the Vietnam War from 1961 to 1971. During this time, the military sprayed nearly 80,000,000 litres of toxic chemical and defoliants mixed with jet fuel in Vietnam, eastern Laos and parts of Cambodia. The supposed goal being to destroy forested and rural land, depriving guerrillas of cover and to induce forced-draft-urbanisation, destroying the ability of peasants to support themselves, forcing them to flee to the cities dominated by US forces, depriving the guerrillas of their rural support base and food supply...
An Unjustifiable Risk investigates the many risks of plutonium usage in nuclear power generation and the use of fast-breeder reactors argued for the UK in the 1970s. The film turns to Hiroshima, Japan to illustrate the powerful destructive capacities of plutonium, feeding-back the personal experiences of those effected by nuclear weapons into the debate against nuclear power and its consequences...
Atomic Confessions investigates the devastating effects of atomic weapons testing carried out in Australia by the British military during the 1950s. Members of the Australian Army, Air Force and Navy detail former top-secret aspects of the tests, while prominent Aboriginal Elders describe the real impacts on the ground. Using archival film and photographs, as well as eye witness accounts, Atomic Confessions chronicles the consequences of nuclear testing imposed on the Australian people, and the land, showing that these tests are not just skeletons of the past...
Atomic Footprints uses archival footage and new material from the outback of Australia to examine the nuclear fuel chain, and the current push to expand uranium mines throughout Australia. This film speaks with local indigenous communities about the impact of already-existing uranium mining and refinement, and shows in clear examples some of the reasons why we should continue to oppose it around the world.
By charting the history of the anti-war movement against the political backdrop of the atomic age, Beating The Bomb examines the current state of 'nuclear deterrence' brought about by the nuclear age stemming from the end of World War II, when the United States nuked Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Specifically, the anti-nuclear movement and the founding of the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament in 1958 amongst others, fight for and end to the British Nuclear Weapons program, which from its inception, was closely tied to The Manhattan Project and still is to this day...
On April 26, 1986, the worst nuclear accident in history occurred when a reactor exploded at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in Ukraine, releasing 90 times the radioactivity of the atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Sixteen years later, Chernobyl Heart travels to ground zero, following the devastating trail radiation leaves behind in hospitals, orphanages, mental asylums and evacuated villages. The film reveals those hardest hit by radiation, including thyroid cancer patients and children suffering from unfathomable congenital birth and heart defects, still decades later...
Fire and Water
In 1983, the Australian Government approved the construction of Olympic Dam uranium mine at Roxby Downs in central South Australia, despite overwhelming opposition by the traditional indigenous land owners—the Kokotha and Arabunna people—and other Australian's in the community. With an approval for expansion of the mine 14 years later, this film documents one of the many events organised in protest of the mine, as well as other actions to raise awareness of the many impacts of uranium mining in Australia.
On 11th March 2011, a 9.0 magnitude earthquake unleashed a devastating tsunami destroying whole Japanese towns and villages. It also hit the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, damaging four reactors and leaking radiation. As the toxic fallout affects the health, safety and livelihood of millions, Japan faces its biggest-ever backlash towards nuclear power. Anti-nuclear activism in Japan has been on the rise along with calls for changes in energy policies generally. And from being the world's third-highest user of nuclear energy, the country now has only five of its 54 reactors working, but lengthened the time-span of its oldest reactors by 20 years. What's going on?
Every day, the world over, large amounts of high-level radioactive waste is placed in interim storages which are vulnerable to natural disasters, human-caused disasters, and societal changes. In Finland, the world's first 'permanent' repository is being hewn out of solid rock--a huge system of underground tunnels that must last hundreds of thousands of years. Once the waste has been dumped and the ground is full of this waste, the land is to be sealed off with concrete and "never be opened again." Or so the builders of this dump can hope. But can they ensure that? How is it possible to warn future generations of the deadly waste that's left behind by this culture? How do we prevent future generations from thinking they have found the 'pyramids' of our time, mystical burial grounds, or hidden treasures? Into Eternity is a film about the insanity of nuclear power and the consequences that have impacts for hundreds of thousands of years.
In 1986, a catastrophic nuclear accident occurred at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine. An explosion and fire released large quantities of radioactive contamination into the atmosphere, which spread over much of Western USSR and Europe. Life After Chernobyl uses this event to show how wild nature reacts and survives when the world is suddenly rid of the impacts of industrialisation. Travelling to the site of Chernobyl, animals return, forests regrow, buildings disintegrate into grass -- perhaps saying in a rather horrific way that a nuclear accident is better for the natural world than industrial civilisation...
Mr Nixon's Secret Legacy covers the absurdity of the supposed logic behind "Mutual Assured Destruction" or MAD--a doctrine of military strategy and the national security policy of the United States during the cold war. During this time, MAD is supposedly disassembled, but replaced with a strategy called "Counterforce." This film investigates the propositions of "Counterforce," questioning the rhetoric of executing a "flexible, acceptable nuclear war."
On 8th August 1945, the United States dropped its second atomic bomb on Nagasaki, Japan, three days after the bombing of Hiroshima. The city was a veritable apocalyptic vision, devastated by this new type of weapon. Nagasaki -- The Horror Of Fat Man documents the memories of survivors, both Japanese civilians and Western Prisoners Of War, as they relate the morbid aftermath of the bombings, the United States occupation, and the segregation that still effects fallout victims to this day.
In July 2005, the Australian government announced its plan to open a radioactive waste-dump facility in one of three Department of Defence sites in the Northern Territory of Australia. With widespread community resistance by the indigenous people of the territory, No Where Here in the Middle documents the ongoing story of resistance to the dump and the fight to be free of toxins, poison, and a brutal occupation.
On 11th March 2011, a huge tsunami, triggered by an 8.9 magnitude earthquake, hits Japan. It cripples the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, releasing radiation, and turning the residents of Futaba into nuclear refugees. The devastation experienced by the town--dead livestock, crops abandoned, homes destroyed--was infinitely worse than anything reported by the newspapers. A year later, many refugees are still unable to return to homes that will be contaminated for many hundreds of years. The irony of this disaster occurring in a nation that experienced two nuclear bombs is not lost on the victims who poignantly question their responsibility for striking a Faustian bargain with nuclear power. Nuclear Nation examines the tragedy of Fukushima, and also whether it could one day be replicated on a grand scale.
Nuclear Nation II is Atsushi Funahashi's sequel, documenting the consequences of the March 2011 nuclear disaster at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Japan. In this follow-up, we learn that the former mayor--previously a fervent advocate of nuclear energy and now a passionate fighter for the victims of the catastrophe--has now been replaced by someone younger. The single-minded cattle breeder also makes another appearance, originally having resisted the government's orders to evacuate the disaster zone and kill his livestock. Today, a look at his animals lays bare the consequences of radioactive contamination: they all have ulcers and open wounds. It wasn't until late 2014 that the final people left the school building, but they're unlikely ever to be able to return to their homes. The epicentre of the catastrophe has been declared a toxic waste disposal site. The inhabitants of Futaba, to whom nuclear energy once brought affluence, are now paying the high price for it.
How does one sell a war? This was a question that weighed heavy on the minds of those in the United States government long before the invasion even started. Operation Saddam: America’s Propaganda Battle takes a look at the marketing of war -– a cocktail of distortion, lies and forgeries -– as shown by former secret service agent Ray McGovern, American investigative journalist Seymour Hersh and best-selling author John MacArthur, presenting the individual stages of the propaganda battle, by which American, British and other governments sought to justify the second invasion of Iraq...
Pandora’s Box
Pandora's Box -- A fable from the age of science, is a six part series examining the consequences of political and technocratic rationalism, tying together communism in the Soviet Union, systems analysis and game theory during the Cold War, economy in the United Kingdom during the 1970s, the insecticide DDT, Kwame Nkrumah's leadership in Ghana during the 1950s and 1960s and the history of nuclear power.
Just along the fault lines of the Pacific Rim of Fire from Japan, lies Taiwan--another heavily industrialised, modern economy highly reliant on nuclear power. Ninety percent of the world's earthquakes occur along the Rim of Fire, so no wonder there are worries about a fourth nuclear plant being built there. The government of Taiwan is promising to hold a referendum on its future, but if the reactor doesn't go ahead the country's nuclear strategy is in question, along with the $9 billion already spent on the plant. And the state-owned power company, Taipower, would face bankruptcy, leaving no one to manage Taiwan's nuclear waste. The waste currently sits across the water on the tiny Orchid Island, quickly corroding and risking potential disaster for the native Tao inhabitants. As fears grow, can we learn from Fukushima before it's too late?
Stop the Flows is a media project in progress to document resistance movements around the world that are working towards stopping the flows of oil and gas, minerals and other natural 'resource' extraction from within their communities, territories and landbases; as well as stopping the flow of the tremendous amounts of wealth generated from these destructive activities. This series aims to support and capture the many forms of organising, direct-action, protest and resistance movements throughout the world working to end mining, the oil economy, nuclear power and more...
In 2010, the United States announced the construction of the first new nuclear power plant in more than 30 years. But a year later in Japan, a 9.0 magnitude earthquake hit, preceding a cataclysmic meltdown at the Fukushima Daiichi Power Plant bringing the reality of nuclear power back into public consciousness across the globe. For some. Both political parties of the United States ignored this and continued a pro-nuclear agenda, while others, forgetting more of the past, didn't realise the history of home. The Atomic States of America serves to break this forgetting by travelling from the gates of Three Mile Island, to the cooling ponds of Braidwood to document just some of what has happened and is happening with nuclear power in the United States today. By speaking with communities throughout the country, this film documents arrays of stories of polluted drinking water, government collusion with industry, cover-ups, cancer epidemics and other suppressed stories. Begun more than a year before the disaster in Japan, this film gains a unique before and after perspective, seeking to inspire an honest remembering about just what this culture has done and continues to do for power at the expense of the world.
The Battle Of Chernobyl recounts the most significant and catastrophic nuclear explosion in history -- an incident that was kept secret for twenty years by the Soviet Union and United States alike. More than 200 people died or were seriously injured by radiation exposure immediately after the explosion and many generations later, the impacts are still felt in cancers, birth defects and toxic ecology, with millions of people still suffering from radiation related health problems such as leukaemia and thyroid cancer...
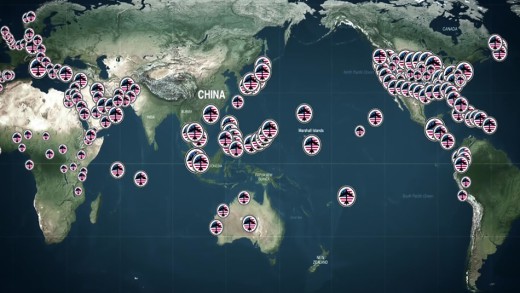
The Coming War on China is a warning that nuclear war is not only imaginable, but a 'contingency,' says the Pentagon. The greatest build-up of NATO military forces since the Second World War is under way on the western borders of Russia, and some 400 American military bases encircle China with missiles, bombers, warships and nuclear weapons. But these happenings are of course not reported as United States antagonism. Instead, there is a familiar drumbeat of war, the kind of the old "yellow peril," a restoration of the psychology of fear that embedded public consciousness for most of the 20th century. The aim of this film is to break the silence, and as the centenaries of the First World War presently remind us, horrific conflict can begin all too easily. By recounting the secret and forgotten history of the rapacious actions of great power against China throughout the decades, such as the destruction of the Marshall Islands and the Opium wars, The Coming War on China is also a report of an inspiring popular resistance to nuclear weapons, military bases and warmongering of the United States, of which little is known in the West.
The Nuclear Comeback embarks on a tour of the nuclear industry, documenting some of the most 'famous' nuclear facilities worldwide -- the control room of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, the UK's Calder Hall, a nuclear waste repository under the Baltic Sea, the Ranger uranium mine in Australia, and one of only two nuclear waste "recycling plants" in the world. In addition of the links to nuclear weapons, the nuclear industry has a reputation for accidents and cover-ups. What are the 'risks'? What to do with the 100,000+ year legacy of dangerous radioactive waste? Is this insane?
When the United States devastated Hiroshima and Nagasaki with nuclear weapons in 1945, the bombs dropped were code-named 'Fat Man' and 'Little Boy' -- as part of the new propaganda campaign to create acceptable images of war, propagating the illusion that the world should live securely with nuclear weapons, and that it is the only way to 'enable peace'. By using reassuring and even soothing language, this new kind of propaganda spread all over the world...
The insane and horrific history of the development of nuclear weapons is examined first-hand in Trinity and Beyond. The film makes use of extensive archive footage from declassified military sources, where the sources themselves speak about the development of nuclear weapons, revealing the calamitous results of use. From the United States's Trinity test of 1945, to the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki; to the rapid increase in testing and proliferation by states across the globe, culminating to the first Chinese atomic bomb test in 1964, Trinity and Beyond is a stark reminder of this culture's insanity and death urge, and how—unless it is stopped—the expanding threat it continues to pose draws in, literally, the prospect of life on this planet for generations to come.
Uranium
Focusing specifically on mines in Canada, Uranium examines the hazards of uranium mining, the toxic and radioactive waste involved at every stage of the process, as well as the wholistic way that indigenous communities have been violated and destroyed by mining and refining practices throughout the country and the world...
In Europe, nuclear energy is popularly touted as supposedly the best way to "save the climate." But what's wrong with that argument? Nuclear power stations run on uranium and the by-products are harmful, toxic and controversial for hundreds of thousands of years, not to mention the many dangerous effects of mining for the mineral on the environment and humanity...
60 years after the United States dropped nuclear weapons on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in Japan, the events are still espoused with denial and myth in histories taught by the west. White Light, Black Rain breaks this acquiescence and accounts the bombings from the point of view of the people who were there, speaking with survivors of the attacks and four American military men that were intimately involved in dropping the bombs. The film intimately details the human costs of warfare and stands as a powerful warning that with enough present-day nuclear weapons worldwide to equal 400,000 Hiroshimas, we cannot afford to forget what really happened with these events.