Just along the fault lines of the Pacific Rim of Fire from Japan, lies Taiwan--another heavily industrialised, modern economy highly reliant on nuclear power. Ninety percent of the world's earthquakes occur along the Rim of Fire, so no wonder there are worries about a fourth nuclear plant being built there. The government of Taiwan is promising to hold a referendum on its future, but if the reactor doesn't go ahead the country's nuclear strategy is in question, along with the $9 billion already spent on the plant. And the state-owned power company, Taipower, would face bankruptcy, leaving no one to manage Taiwan's nuclear waste. The waste currently sits across the water on the tiny Orchid Island, quickly corroding and risking potential disaster for the native Tao inhabitants. As fears grow, can we learn from Fukushima before it's too late?
The oil industry giant Chevron began operating in Ecuador's Amazon rainforest in 1964, and by the time the corporation fled the area in 1992, their toxic footprint had brought about 1,700 times more damage than the infamous Exxon Valdez oil spill in the United States in 1989. Chevron vs. The Amazon visits the scene of this epic and enduring crime, to uncover the acts that have killed the riches of the world's tropical paradise. The Amazon is home to hundreds of thousands of unique species of plants, animals, insects, landscapes, as well as an equally diverse human population—all under severe and continued stress and threat. Chevron dumped 17 billion gallons of crude oil and 19 billions gallons of contaminated waste water into the Amazon. Prior to fleeing, they attempted to hide this by covering the areas with dirt or setting the toxic dumps on fire. This film shows the totality of these crimes, and how the land and its people have suffered from devastating impacts over the ensuing decades, as the first step to holding corporate criminals to account, for justice and the survival of the Amazon and its peoples.
Despite decades of environmental impacts and campaigning for bans and other regulations, the plastic industry continues to expand. From 1990 to 2010 alone, production of plastics more than doubled. Fracking has provided cheap natural gas which is also driving down the cost of making plastic. The United States is now one of the world's largest plastic producers, and industry is investing tens of billions of dollars in new plastic plants. By 2050, it's estimated that global production of plastic will triple. Alongside, the industry has pushed a greenwashing image of recycling to fend off negative public opinion, and sell more plastic. Plastic Wars examines how this has come to be, using industry documents and former insiders, and presents the urgency of the need for change, now more than ever.
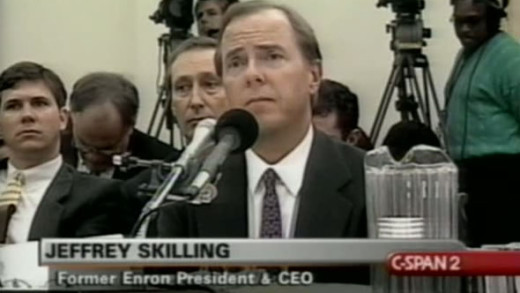
In 2001, the collapse of the Enron Corporation was of one of the largest business scandals in American history. The collapse resulted in criminal trials for several of the company's top executives, bringing the facts of exposure to Enron's involvement in the California electricity "crisis," where the company had rigged the market in order to generate huge speculative profits during the power shortages and blackouts of the time that effected millions of people.
For years, the Earth Liberation Front--autonomous individuals operating in separate anonymous cells without any central leadership--carried out spectacular direct-actions against businesses that destroy the environment. Some of the targets were logging corporations, SUV dealerships, ranger stations, a slaughterhouse and a multi-million dollar ski-lodge at Vail, Colorado that was expanding into national forest. As authorities were not able to crack the case and disbanded many years later, the FBI got lucky when they were led to a former activist who agreed to co-operate with them and become an informant. If A Tree Falls provokes hard questions about environmentalism, activism, and the way 'terrorism' is defined by following the story of the activists who were turned over to the FBI, and their fate...
Exempt from environmental protection laws, the oil and gas industry has left idyllic landscapes and rural communities throughout the United States pockmarked with abandoned homes, polluted waterways and aquifers, as well as plenty of sick people. Split Estate zeroes in on Garfield County in Colorado, and the San Juan Basin where more demonstrations of water that can be set on fire are found, but industry isn't just stopping there -- fracking is spreading across the United States, with plans to even drill in the New York City watershed, as well as elsewhere around the globe. As the appetite for fossil fuels increases, Split Estate debunks claims by an industry that assures the public that it is a good neighbour, driving home the need to stop fracking, both here and abroad...
Aluminium is everywhere—beer cans, tinned food, cooking pans, computers, pens, cosmetics; and many medications, including most vaccinations. Though what do we know about this material? The Age of Aluminium profiles people whose health has been seriously impacted by unwitting exposure to aluminium; along with research exploring how aluminium as a known neurotoxin relates to the growing epidemic of chronic illnesses and disabilities such as breast cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, allergies, and autism. Aluminium mining and manufacturing have also created cataclysmic environmental problems in several parts of the world, as we see the devastating effects of aluminium mining in South America, and environmental disasters in Hungary and the UK. What are we doing with this material? And what can we do now to avoid the continued impacts on our lives and the natural world?
On 11th March 2011, a huge tsunami, triggered by an 8.9 magnitude earthquake, hits Japan. It cripples the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, releasing radiation, and turning the residents of Futaba into nuclear refugees. The devastation experienced by the town--dead livestock, crops abandoned, homes destroyed--was infinitely worse than anything reported by the newspapers. A year later, many refugees are still unable to return to homes that will be contaminated for many hundreds of years. The irony of this disaster occurring in a nation that experienced two nuclear bombs is not lost on the victims who poignantly question their responsibility for striking a Faustian bargain with nuclear power. Nuclear Nation examines the tragedy of Fukushima, and also whether it could one day be replicated on a grand scale.
In Europe, nuclear energy is popularly touted as supposedly the best way to "save the climate." But what's wrong with that argument? Nuclear power stations run on uranium and the by-products are harmful, toxic and controversial for hundreds of thousands of years, not to mention the many dangerous effects of mining for the mineral on the environment and humanity...
Following up from The End Of Suburbia, this film examines the rich interplay on the subtle relationships between the energy crisis, neighbourhood gardens and the collapse of the 'American dream'. Escape From Suburbia outlines potential solutions with interviews from individuals across the world who are brave enough to challenge their communities toward change...
Fracking In America takes a look at the continuing instances of water contamination and environmental damage occurring throughout the United States as a result of hydraulic fracturing--an industrial process used to fracture rock in the search to exploit natural gas deposits. As the frantic effort to extract gas accelerates, the impact of fracking expands also, with increasing pressures on fresh water supplies, continuing threats to health and wider ecosystems...
A new gold rush is sweeping through the Amazon rainforest where scores of people are bustling in to hunt for the last nuggets and specks of gold. This insatiable rush is perpetuating the further destruction of one of the largest remaining tropical forests in the world; bringing with it weapons, mercury, crime and alcoholism, and turning once pristine creeks and rivers into dumping grounds for mining. In the forest also lies the story of the Wayanas, a Native American tribe from Guiana, who are being poisoned by the mercury releases from the mining. Their communities are enduring one of the world's worst globalisation disasters, fighting back against all odds.
Decades of over-fishing by the global tuna industry have now pushed the final frontiers to the waters of Papua New Guinea. In the 1950s, commercial fishing was extracting 400,000 tons of tuna from the ocean. This number is now close to 4 million tons. And it comes at a high cost: a human one, now affecting the last places on Earth to receive the full impact of globalisation. Set in "the land of the unexpected," in the north-eastern part of Papua New Guinea, Canning Paradise follows the struggle of Indigenous tribes to protect their way of life, guarded by traditions dating back since the beginning of time. While many have lost hope, others are fighting for survival from the corrupt government and the omnicidal dominant culture.
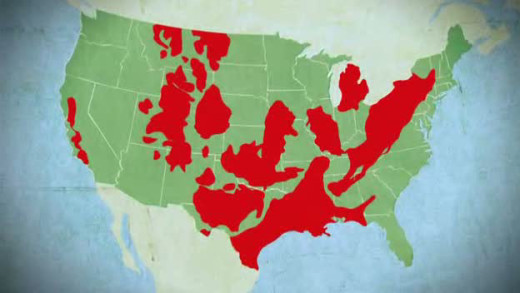
America's largest domestic natural gas drilling boom is in full swing and the Halliburton corporation claims it has refined a technique called 'hydraulic fracturing' that extracts natural gas in a "safe and environmentally friendly way". But upon examination, film-maker Josh Fox uncovers a trail of secrets, lies and first-hand evidence of intense water contamination and devastating environmental destruction...
Plastic Planet is an up close and detailed examination of one of the most ubiquitous materials of our age, the plastic age. This controversial and fascinating material has found its way into every facet of our lives, literally. Plastic Planet takes us on a journey around the world, showing that plastics are a threat for human health and the ecosystems of the planet...
The Prize: The Epic Quest for Oil, Money, and Power is an 8-part series based on Daniel Yergin's book by the same name, that captures the panoramic history of the largest industry in the world and traces it's changing face over the decades. Each episode in the series focuses on an era of oil, from beginning to today; while examining the connections and ramifications of an industry that literally transformed global political and economic landscapes--while continuing to make its mark...
How to Let Go of the World and Love All the Things Climate Can't Change travels the globe, from New York City to the Marshall Islands and China, to meet with people who are committed to reversing the tide of global warming. The film examines the intricately woven forces that threaten the stability of the climate and the lives of the world's inhabitants.
For years, regulatory agencies and environmental groups have insisted that the increase in whale deaths off the East Coast of the United States has nothing to do with the rapidly-expanding wind industry's high-decibel pile driving, sonar mapping, and boat activities, to install wind-harvesting facilities for electricity generation. Thrown To The Wind travels to parts of the ocean where these activities are underway, to investigate these claims, showing that indeed these industrial activities are impacting critically endangered species in profound ways--which are being systematically ignored, while the climate and ecological crisis rages.
The myths of globalisation have been incorporated into much of our everyday language. "Thinking globally" and "the global economy" are part of a jargon that assumes we are all part of one big global village, where national borders and national identities no longer matter. But what is globalisation? And where is this global village? In some respects you are already living in it. The clothes in your local store were probably stitched together in the factories of Asia. Much of the food in your local supermarket will have been grown in Africa...
Testify: Eco-Defence And The Politics Of Violence examines the forces that drive revolutionary environmental activism, using examples of direct-actions from the Animal Liberation Front (ALF) and the Earth Liberation Front (ELF) to illustrate tactics...
Fracking Hell -- The Untold Story looks at the risks of natural gas development in the Marcellus Shale throughout the United States. From toxic chemicals in drinking water to interstate dumping of radioactive waste that cataclysmically contaminates water supplies, to fracking plans in major population centres including New York City -- are the health consequences worth the supposed economic gains?
The Idiot Cycle investigates six major chemical companies—Dow Chemical, BASF, Bayer, Dupont, Astrazeneca and Monsanto—that are not only responsible for producing decades of cancer causing chemicals and pollution all across the globe, but also profit extensively from controlling cancer treatments and the production of drugs for those treatments. The irony is palpable. Also examined is how these very same companies own the most patents on genetically modified foods that have also never been tested for long-term health impacts like cancer. When there's dioxin in every mother's breast-milk, rivers throughout the world that no longer support life, cataclysmic environmental damage from industry and manufacturing—when do we say enough is enough?
Nuclear Nation II is Atsushi Funahashi's sequel, documenting the consequences of the March 2011 nuclear disaster at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Japan. In this follow-up, we learn that the former mayor--previously a fervent advocate of nuclear energy and now a passionate fighter for the victims of the catastrophe--has now been replaced by someone younger. The single-minded cattle breeder also makes another appearance, originally having resisted the government's orders to evacuate the disaster zone and kill his livestock. Today, a look at his animals lays bare the consequences of radioactive contamination: they all have ulcers and open wounds. It wasn't until late 2014 that the final people left the school building, but they're unlikely ever to be able to return to their homes. The epicentre of the catastrophe has been declared a toxic waste disposal site. The inhabitants of Futaba, to whom nuclear energy once brought affluence, are now paying the high price for it.
Is the world heading for a population crisis? Since 1950, the human population has more than doubled. What is the effect of this rapid growth on the environment? While much of the projected growth in human population is likely to come from the so-called "developing world," it is the lifestyle enjoyed by the West that has the most impact--in the UK consumers use as much as two and a half times their fair share of Earth's resources. This film examines whether it is the duty of individuals to commit not only to smaller families, but to change the way they live for the sake of humanity and planet Earth.
The Garden
The Garden tells the story of South Central Farm -- a 14 acre community garden and urban farm located in Los Angeles, California, which was in operation between 1994 and 2006. The entire lot is evicted and demolished against overwhelming local support for the farm and also despite the community raising an incredible amount of money to purchase the land from the owner. The owner refuses to sell and the land is demolished and still sits vacant, unused...
China's factories provide low cost products such as computers and cars to the rest of the world, but the real cost is high with heavy air pollution, contaminated waterways, decimated land, terrible working conditions, widespread cancer and incidences of deaths. China's Dirty Secrets travels across the country to follow workers at factories that assemble computers, then to e-waste dumps, and finally an industrial incinerator burning medical waste, all showing first-hand the extensive environmental impacts of so-called "economic growth."
DamNation
Travelling across North America, DamNation investigates the growing change in national attitude from strange pride in big dams as domineering engineering projects, to the growing truthful awareness that dams have always been the great killers of rivers, wildlife, the salmon, the forests, coastlines, watersheds. Life is bound to water and health of rivers, and now, dam removal in many forms—including Monkey Wrenching—is reclaiming that life and spreading. Where dams come down, rivers come back, allowing the salmon to return after decades of being concreted out. By making firsthand unexpected discoveries moving through rivers and the landscapes altered by dams, DamNation presents a much-needed metamorphosis in values, from conquest of the natural world to knowing ourselves as part of nature; to respect, and be humbled. With over two million dams in North America alone—75,000 of them over six feet tall—there's much work to be done. Let's get to it.
One More Dead Fish reveals how destructive industrial fishing practices have decimated the Grand Banks of the North Atlantic Ocean, once an abundant area of food. The film also tells the dramatic story of how local hook-and-line fishermen are battling huge commercial fishing practices in order to survive in a globalised fishing industry. In interviews with local fishermen, government officials, biologists, and industry CEO's, the film explores regulatory, legislative, and environmental issues. The film grounds the viewer in a clear historical context as it explains one of the world's great environmental disasters. In examining the twisted language of the multinational fishing industry, One More Dead Fish questions why we don't hear more about the true environmental costs of industrial fishing practices, partly the result of globalisation.